Phishing Attack:
Phishing is a kind of Social Engineering attack, where the attackers can able to gather information about any individual person or group of organizations using deceptive e-mails and websites. The goal of the phishing attack is to steal sensitive and confidential information such as login information like usernames, passwords, credit card information, network credentials, or to install malware on the targeted machines.
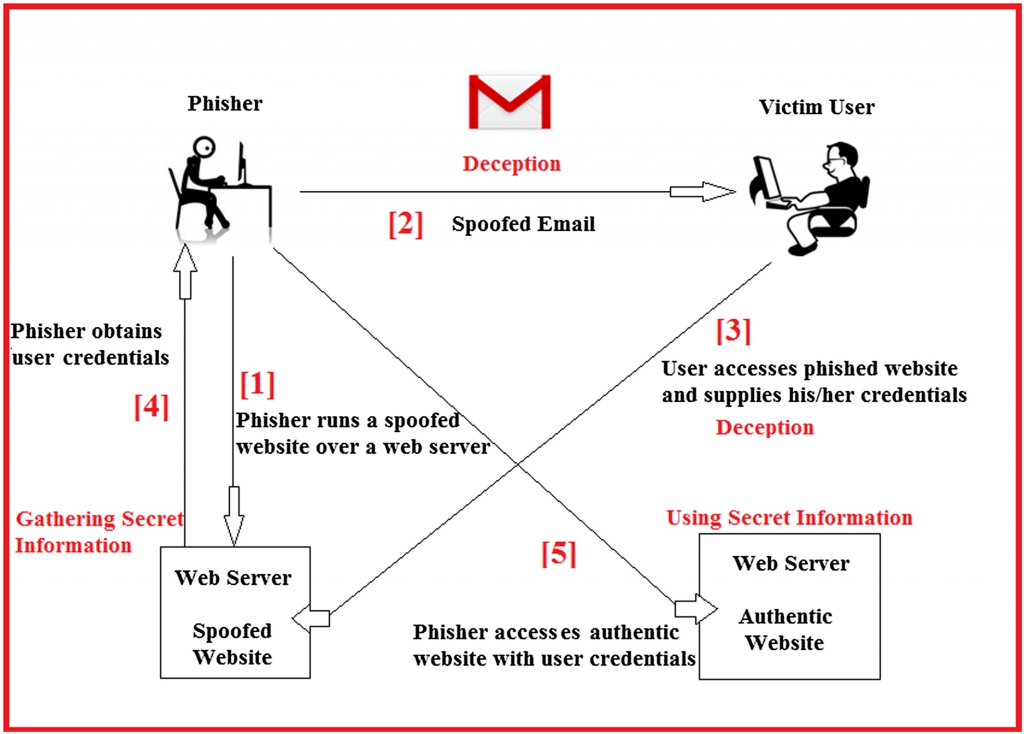
How does Phishing works?
Initially, When the attacker tries to connect the victim machines by sending a fraudulent email or other communication. Usually, posing as a legitimate company and with the help of this, they attempt to gain any personal information or login information from the target. Sometimes malware is also downloaded onto the target’s computer.
Most of the phishing attacks come via email, but they aren’t the only medium for phishing attacks. It can also occur via instant messages, social media or even search engine ads, etc., Only common is that they include a link to a website, which then tries to get you to give away your login credentials to a specific website, or to surrender your private data such as social security details or bank card number.
Example1: Sometimes you could receive an email from the software you use, telling you that your subscription is running out of date, asking you to continue the subscription by entering your credit card details. The party asking for your credit card detail is a scammer, who will use your credit card information.
Example2: Some kind of phishing email could also “warn” you that your password to a software or application is getting out of date, and they will ask you to create a new password. As you add in your old and new password, the phishers gain access to your old password in the software or program and use this to log in and gain your private information.
Common Types of Phishing Attacks:
● Email phishing.
● Deceptive phishing
● Spear phishing.
● Whaling.
● Smishing and vishing.
● Angler phishing.
Email phishing:
Most of the phishing attacks are done by email. The Phisher will register a fake domain that will act as a genuine organization and sends thousands out thousands of generic requests. For Example, The fake domain often involves character substitution, like using ‘r’ and ‘n’ next to each other to create ‘rn’ instead of ‘m’.
Deceptive phishing:
Deceptive phishing is the most common type of phishing. In this case, an attacker attempts to obtain confidential information from the victims. Attackers use the information to steal money or to launch other attacks. A fake email from a bank asking you to click a link and verify your account details is an example of deceptive phishing.
Spear phishing:
Spear phishing targets specific individuals instead of a wide group of people. Attackers often research their victims on social media and other sites. That way, they can customize their communications and appear more authentic. Spear phishing is often the first step used to penetrate a company’s defenses and carry out a targeted attack.
Whaling:
When attackers go after a “big fish” like a CEO, it’s called whaling. These attackers often spend considerable time profiling the target to find the opportune moment and means of stealing login credentials. Whaling is of particular concern because high-level executives are able to access a great deal of company information.
Smishing and vishing:
Both smishing and vishing, telephones replace emails as the method of communication. Smishing involves criminals sending text messages (the content of which is much the same as with email phishing), and vishing involves a telephone conversation.
Angler phishing:
A relatively new attack vector, social media offers a number of ways for criminals to trick people. Fake URLs, cloned websites, posts, and tweets, and instant messaging (which is essentially the same as smishing) can all be used to persuade people to divulge sensitive information or download malware.
How to Prevent Phishing Attacks:
● Protect your computer by using security software because it will scan every file which comes through the Internet to your computer.
● Protect your mobile phone by setting software to update automatically and Don’t ignore those updates.
● Protect your accounts by using multi-factor authentication for confirmation—something you know (i.e., password).
● Protect your data by backing it up regularly.
● Never share your credentials.
● Don’t give your information to an unsecured site.
● Get free anti-phishing add-ons.
● Don’t open unknown emails from untrusted domains.
● Usually, fake domain often involves character substitution, like using ‘r’ and ‘n’ next to each other to create ‘rn’ instead of ‘m’.
● Check the spelling and grammar content of the email.
● Scan the Email attachments, whenever it’s possible.
● Reset your passwords regularly.
● Install firewalls: Firewall protection prevents access to malicious files by blocking the attacks.
● Don’t be tempted by those pop-ups, read them completely.
● Don’t give out important information unless you must.
● Use some Data Security platforms to spot signs of an attack.
Conclusion:
We all know that Phishing is a greater platform for fraudulent attempts to steal sensitive information about any individual or group of organizations. So we should aware of some of the common Phishing attacks and we should know the importance to safeguard ourself and online users from becoming victims of online fraud. Therefore, Phishing detection tools play a vital role in ensuring a secure online experience for users.



































