We have already discussed how SPF, DKIM & DMARC will function in the email gateway. Here we are going to see two use cases of how the DMARC record will be logged if an email is sent from the existing user and a non-existing user. We readily have more online tools to learn how DMARC works. One of the best tools from which I learned is emkei. Emkei.cz is a free online fake mailer with attachments, encryption, HTML editor, and advanced settings.
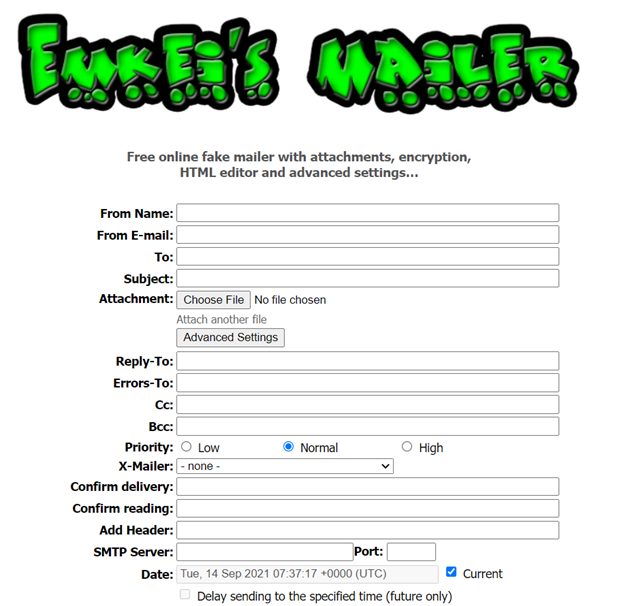
Fields in the console:
- From Name: Name of person from which you are sending the email. Put the senders Name there.
- From Email: Need to type the Email sender that is from which email address you are ging to sending fake or anonymous email.
- To: In this box put the email address that you want to send the fake mail.
- Subject : In this box here you have to enter the subject of email that you want to send, it’s like subject of normal emails.
- Attachment: Select the file that you want to attach.
- X-mailer: Select the service from which you want to send.
- Content type: Text/Plain or Text/Html: If you want to send normal text mail select text/Plain and if you want to send phish mails then you need to select Text/Html.
- Text : Here you have to enter the message you want to sent in fake mail.
Use Case 1:
Email sent from Non-Existing id:
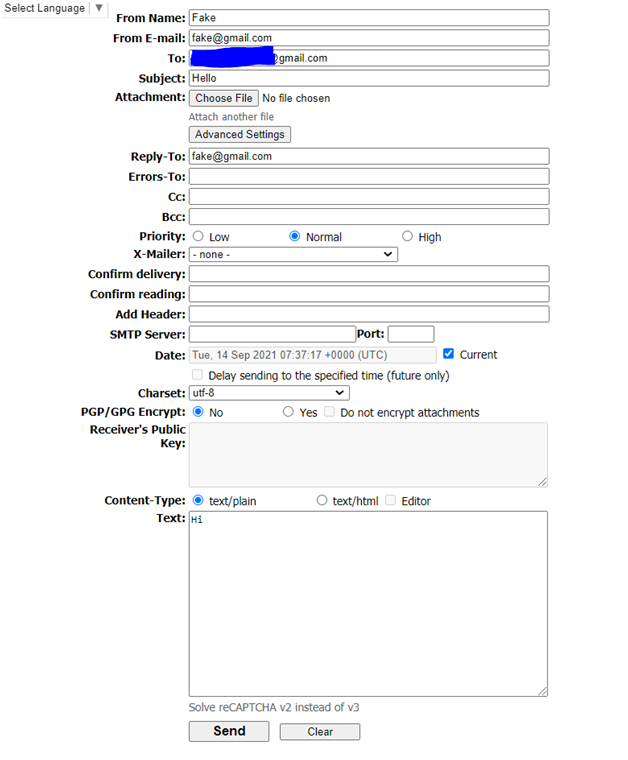
- Updated the “From E-Mail”& “Reply-To” field as [email protected] which is a non-existent email id.
- Updated the “To” field as a****[email protected] which is an existing email id.
- Updated the subject as “Hello” & Test as “Hi”.
Below is the screenshot of the fake email webpage:
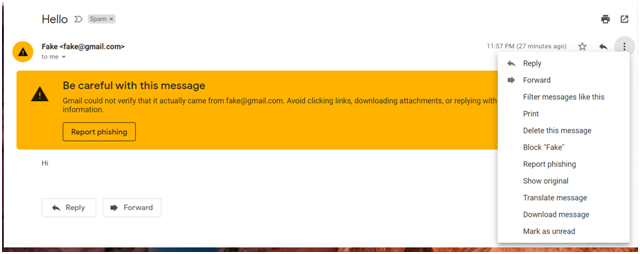
Analysis:
After sending the email, we have observed the following changes:
- The email was not received to Inbox. It landed in SPAM folder.
- Analyzed the header of the email by clicking the “Show original” in Gmail.
Also Read: APT-Hunter – Threat Hunting Tool For Windows Event Logs
- The SPF seems to be “SOFTFAIL”and DMARC is “FAIL”.
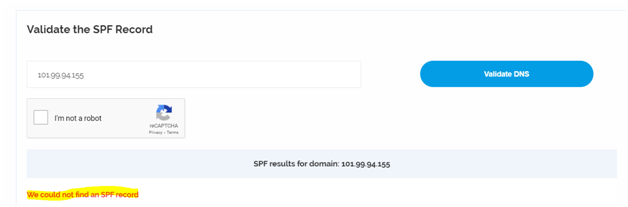
- SPF Details:
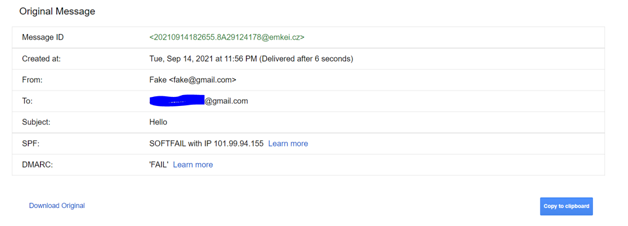
Here the IP seems to be 101.99.94.155 which belongs to the Hostname: emkei.cz. Checked the SPF record for this IP and found that there is no DNS record for it. Hence it got soft failed.
- DMARC Details:
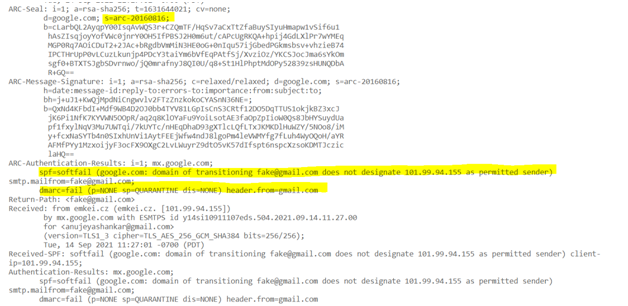
Since the SPF fails with the error message as “sender email id does not designate the IP as permitted sender”, the email doesn’t check the DKIM and straightly selected the Quarantine option.
Also Read: Linux Audit Logs cheatsheet – Detect & Respond Faster
Use Case 2:
Email sent from Existing id:
- For example taking an email from my inbox.
Analysis:
- Analyzed the header of the email by clicking the “Show original” in Gmail.
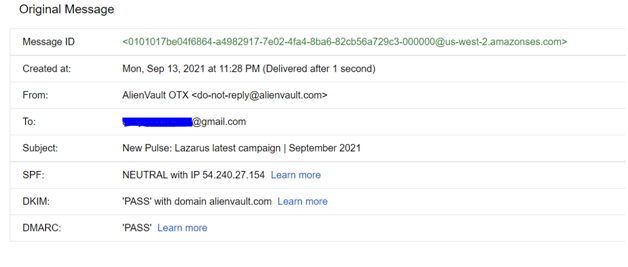
- All the three email protocols are passed and the email landed in INBOX.
- SPF Details: Here the IP seems to be 54.240.27.154 which belongs to the Hostname: amazon.com. Checked the SPF record for this IP and found that there is no DNS record for it. Hence the action is Neutral. SPF neutral messages are sent when the domain owner doesn’t want to assert that the sending IP addresses are authorized.
- DKIM Details:
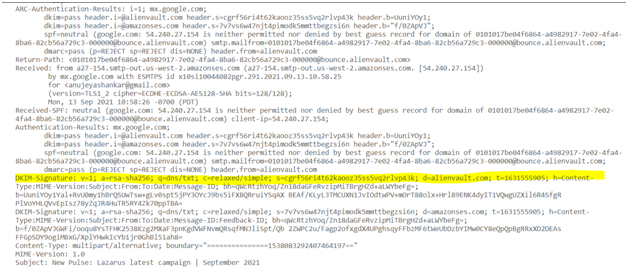
- The above mentioned screenshot is the DKIM signature attached with the email while originating from the sender. Here the keyword “s=cgrf56ri4t62kaooz35ss5vq2rlvp43k”is the DKIM selector which is used to locate and retrieve the public key to verify that the email message is authentic and unaltered in DNS. DKIM will compare the private key obtained from the signature with the public key in the DNS. If it got matches, DMARC will get PASS and land the email in Inbox. Here, SPF is neutral and DKIM got passed. Hence DMARC has landed the email in INBOX.
How to effectively identify a Phishing email?
- The content of the email will be odd if it is from unknown sender. If any customer is compromised and the attackers are trying to send email from that inbox, it will be slightly different from normal emails. This is the first indication of suspect email.
- Spelling mistakes and unofficial template for official things matters the most.
- Sometime the whole email content will be a image. While mouse hovering on it, there will be a malicious link.
- Attackers will say in the email content as they have attached the document. But the document will be inserted in the link.
- Attachments will be a normal Excel file. But macros will be enabled inside it.
- Analyze the headers in thoroughly because the sender and return-path also will be spoofed.
- Urgent email forcing the users to get bank details or SSN or money is the top peak of social engineering.
- Trending fake invoice emails will lead to credential phishing.
- Need to analyze the originating SMTP IP and SPF and DMARC records.
Action items for Phishing emails:
- Need to check whether the email is from external source or from customer. If it is from customer put a hold under email gateway and if it is from external source put a block in email gateway.
- Block all the IOCs associated with the url/attachment. Need to block the redirecting/POST urls in case of credential phishing.
- Delete all the emails from the particular sender incase of external email. For the customer email, delete the email with that subject only.
- Need to check all the IPs/URLs in SIEM/EDR tool to make sure that none of the users have clicked the links.
- For attachments need to check with hash and if incase user has opened the malicious file means, background process will be running in the machine. So alert rules should be stronger to detect such type of activities.
Conclusion:
Identifying the phishing email is not a big deal. We can set up SPF, DKIM & DMARC to automatically reject or quarantine the emails. Organizations can think deeper before enabling any sort of thing for email security.



































