Microsoft Defender Research team reported that they have seen an exponential (256%) raise in XOR.DDOS Linux Trojan attack in their detector platform within 6 months.
It was first discovered in September 2014 by independent Whitehat security research group MalwareMustDie, XorDdos (also known as DDoS.XOR) was named after its denial-of-service-related activities on Linux endpoints and servers as well as its usage of XOR-based encryption for its communications.
Cloud servers and Internet of Things Devices (IoT), which are running with Linux OS are coming targets for this trojan campaign, and after compromise, they are mostly used for DDoS attacks, the biggest of them happened in 2021 and caused 2.1Tbps DDoS attack.
Technical Analysis
First, the trojan tries SSH brute force on thousands of Linux machines at the same time from the already compromised machine, and once it gains an initial foothold. It will download the malicious ELF file using curl and it takes careful measures before and after saving the file, leaving no traces for forensics.
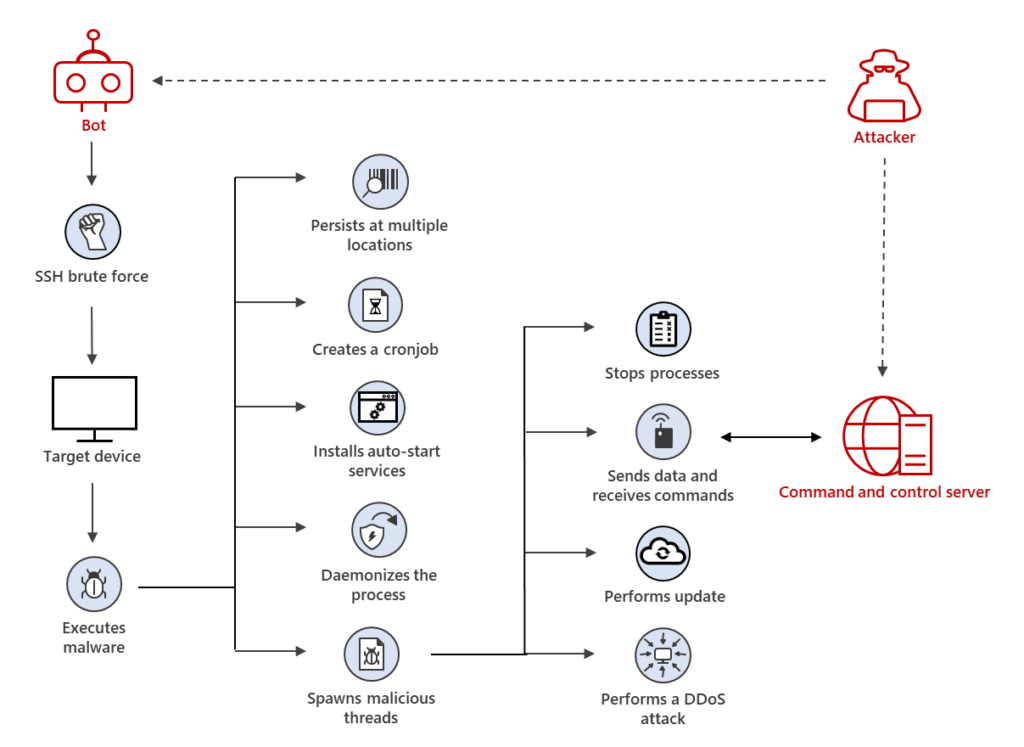
Now, Let’s discuss some of the capabilities of the payload:
- It will add itself in the /etc/init.d and crontab scripts to run the trojan whenever the system starts or run the downloaded payload every X minutes once. So it is a persistent threat.
- The malicious process does not run under users, but under the system and closes itself when the system shutdowns.
- We cannot decode the data on store or transit without a secret key, because It uses XOR-based encryption to obfuscate data.
- Spoofs the process names with face command names to avoid being detected by static rules.
- Some XorDDoS installs rootkits in the kernel to provide root access and hide all trojan-related traces from users. Not only these, but it also provides 12 more features to this trojan.
- It also hides open ports and services from the users using, kernel rootkits. So we won’t see these connections in netstat or any other normal port monitoring tools.
Also Read: Ransomware: How Attackers are Breaching Corporate Networks
Detection Methods
use case 1: Huge Failed sign-in in logins activity traces
- Look for failed log-in attempts across organizations or networks.
- Identify the source system isolate, continue the further investigations and find root causes.
use case 2: Creation of the XorDdos-specific dropped files
- Monitor for the malicious file drops or creations through File Integrity Mentoring
- Monitor for any changes in
"/etc/cron.hourly/gcc.sh", "/lib/libudev.so.6", "/lib/libudev.so"and"/var/run/gcc.pid"
use case 3: Command-line of malicious process
- Monitor for unusual command executions such as
cat resolve.confor any other possible fake commands - Use anomaly detector tools and algorithms to detect unusual behavior in command executions
Prevention Methods:
- Use strong SSH passwords or use private keys for accessing remote servers.
- Deploy File Integrity Monitoring solutions, without FIM capability we won’t be able to tell the changes in sensitive configuration files, like crontab or init.d directories.
- Deploy any network monitoring or visibility solutions
Indicators of Compromises
URLs
- www[.]enoan2107[.]com:3306
- www[.]gzcfr5axf6[.]com:3306
- hxxp://aa[.]hostasa[.]org/config.rar
Known Malicious File Metas
#Hashes
6E506F32C6FB7B5D342D1382989AB191C6F21C2D311251D8F623814F468952CF
CBB72E542E8F19240130FC9381C2351730D437D42926C6E68E056907C8456459
F2DF54EB827F3C733D481EBB167A5BC77C5AE39A6BDA7F340BB23B24DC9A4432
932FEEF3AB6FCCB3502F900619B1F87E1CB44A7ADAB48F2C927ECDD67FF6830A
53F062A93CF19AEAA2F8481B32118A31B658A126624ABB8A7D82237884F0A394
798577202477C0C233D4AF51C4D8FB2F574DDB3C9D1D90325D359A84CB1BD51C
2B4500987D50A24BA5C118F506F2507362D6B5C63C80B1984B4AE86641779FF3
359C41DA1CBAE573D2C99F7DA9EEB03DF135F018F6C660B4E44FBD2B4DDECD39
E6C7EEE304DFC29B19012EF6D31848C0B5BB07362691E4E9633C8581F1C2D65B
EF0A4C12D98DC0AD4DB86AADD641389C7219F57F15642ED35B4443DAF3FF8C1E
B5FBA27A8E457C1AB6573C378171F057D151DC615D6A8D339195716FA9AC277A
D71EA3B98286D39A711B626F687F0D3FC852C3E3A05DE3F51450FB8F7BD2B0D7
9D6F115F31EE71089CC85B18852974E349C68FAD3276145DAFD0076951F32489
360A6258DD66A3BA595A93896D9B55D22406D02E5C02100E5A18382C54E7D5CD
DC2B1CEE161EBE90BE68561755D99E66F454AD80B27CEBE3D4773518AC45CBB7
175667933088FBEBCB62C8450993422CCC876495299173C646779A9E67501FF4
C8F761D3EF7CD16EBE41042A0DAF901C2FDFFCE96C8E9E1FA0D422C6E31332EA
#Possible file names related to XorDDoS trojan
HFLgGwYfSC.elf
gcc.sh
File Locations for Monitoring Changes
/usr/bin/
/lib/
/etc/init.d/
/run/
/tmp/bin
Also Read: Latest IOCs – Threat Actor URLs , IP’s & Malware Hashes
Note: This article is created solely to educate professionals in the cyber frontline to prepare for the old and new threats.



































