An advanced persistent threat (APT) is a smart, protracted cyberattack in which a hacker creates an unnoticed presence in a network in order to steal critical data. An APT attack is deliberately planned and executed in order to infiltrate a specific organization, bypass existing security measures, and remain undetected.
Rather than getting in and out as quickly as possible, the purpose of most APT attacks is to get and keep persistent access to the targeted network. Since APT attacks require a significant amount of effort and resources, hackers often target high-value targets, such as nation-states and large organizations, with the intention of stealing data over an extended period of time.
In order to obtain sustained access, the APT group will use different methods in each stage. In this blog, we are going to elaborate on how the APT group performed the attack and the options used to perform the attack.
Image Source Credits: Will
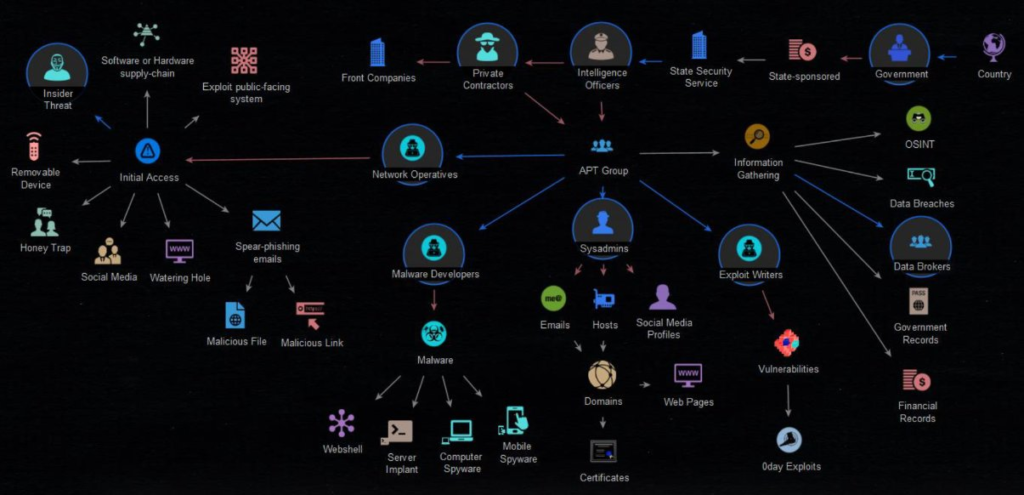
Stage 1: Information Gathering:
In the beginning of every attack, attackers will collect enough information to about the target organization/individuals to perform the attack effectively. The options covered in Information Gathering are:
- OSINT (Open-Source Intelligence)
- Data Breaches
- Data Brokers
- Government Records
- Financial Records
Also Read: Latest IOCs – Threat Actor URLs , IP’s & Malware Hashes
1- OSINT (Open-Source Intelligence):
The technique of gathering information from published or otherwise publicly available sources is known as open source intelligence (OSINT). Attackers use smart way to collect information. So, they will try to fetch it from different websites. “osintframework.com” is one open website where all tools/websites are aligned here to fetch targeted information.
2- Data Breaches:
Hundreds of attacks have compromised the privacy of millions of people in the last few years. A data breach occurs when information is stolen or taken from a computer system without the owner’s knowledge or permission. With the help of the leaked data, attackers will fetch all the valuable information. Data breaches occurs by
- Stolen information
- Ransomware
- Password guessing
- Recording key strokes
- Phishing
- Malware/Virus
- Ddos
3- Data Brokers:
There are many data brokers who quietly buy and sell personal information. It’s no secret that hundreds of firms constantly buy and sell your personal information. Who those companies are and what they do are less known. APT groups will have contact with all these data brokers groups to buy information.
4-Government Records/Financial Records:
Government records are defined as any type of documented information created or received in the process of government business and retained as proof of activities and transactions. Documents that offer evidence of or summarize company transactions are referred to as financial records. The APT group will also obtain information by exploring these documents.
Detection for Information Gathering:
- We can use insights to get alerted if any of the details/usernames & passwords/business documents/financial records/similar organization domains are matches in OSNIT/Dark web.
- Use CTI(Cyber Threat Intelligence) service to minimize and mitigate cybersecurity risks by analyzing, refining, and organizing information gathered from a range of sources about current or potential attacks against an organization.
Stage 2: Initial Access:
After collecting the information, the victim will be trapped via the below options:
- Social Media
- Watering Hole attack
- Honey Trap
- Removable Device
- Insider Threat
- Software or Hardware Supply-chain
- Exploit public-facing system
- Spear-Phishing emails
- Malicious File
- Malicious Link
APT Group will have Network Operatives to get the initial access.
1-Social Media:
Victims will target unattended/active social accounts to get into the system either for organizations or individuals.
2- Watering Hole Attack:
A watering hole attack is a security flaw in which the attacker attempts to compromise a specific group of end-users by infecting websites that the group is known to frequent. The objective is to infect a targeted user’s computer and get access to the target’s workplace network.
An attacker will compromise a web server or web service and implant a malware-laden file, in hopes that their intended victim or victims will access it. Once the trap is set, the visitors to the website or service are infected, and often their devices are also compromised. When a device has become compromised, keyloggers, crimeware, and command-and-control (C2) connections can be leveraged to steal data or even control the device remotely.
Detection/Prevention of Watering Hole Attack:
- Watering hole attacks can be avoided by keeping an eye on your network activities and all external web traffic. It is capable of detecting malicious activities as well as anomalies that may signal an attack.
- Create a rule which will detect the blocked connections towards malicious URLs and continuos connections towards multiple blocked connections. The rule should run for every 15 minutes and set throttling to 1 hr.
- Index=<firewall name> sourcetype=<pan:threat> action=blocked | where count>10| table src_ip, dest_ip, hostname, query, url, action
- A VPN can hide internet activity from outsiders, making it more difficult for attackers to profile targets within your company. A VPN may be required in some circumstances to prevent your employees from accessing unsecured websites such as social media and message boards.
3- Removable device:
Usually, in most organizations, external devices like USB, Pendrive, and hard disks are not allowed. But, in some US organizations, it is allowed. So it is very easy for ATP groups to insert malicious files into external devices while it is connected to one machine and can be transmitted anywhere.
4- Insider Threat:
An insider threat is a security risk that arises from within the target company. It usually involves a current or former employee or business colleague who has unauthorized access to sensitive information or privileged accounts on an organization’s network. Traditional security procedures are often focused on external threats and are unable to detect an internal threat emerging from within the business.
Detections/Prevention of Insider Threat:
- Activity at unusual times, transferring too much data via the network, and accessing unusual resources need to be monitored.
- Try to protect critical assets.
- Clearly document organizational policies so you can enforce them and prevent misunderstandings.
- Deploy solutions to keep track of employee actions and correlate information from multiple data sources.
5- Software or Hardware Supply-chain:
An adversary inserts malicious code or components into a trusted piece of software or hardware in this type of cyber security attack. The goal of such an attack is the ability to infiltrate organizations that are down the chain of the affected component. It is not really an easy process but the famous attacks are done via a Supply-Chain attacks.
Why most ATP groups use this process as the initial stage means, that they can get into many of the systems at a time.
Also Read: Malspam with new Matanbuchus Loader – Detection & Response
Detections/Prevention of Supply-chain:
- Create a rule based on the attack because each attack technique and software will be different.
- Use hash checking or other integrity checking mechanisms to verify distributed binaries. Scan downloads for malicious signatures and try to test software and updates before deploying them.
- Perform integrity checks on pre-OS boot mechanisms that could be modified for malicious intents, and compare the results to a known good baseline.
6- Exploit public-facing system:
Adversaries will target public-facing applications to get into the organization because they don’t need to work more to get into it.
Detections/Prevention of Exploit public-facing system:
Use WAF to detect unusual activities and block all the connections from malicious IPs.
7- Spear-Phishing emails:
This is the common way of initiating any kind of attack. 90% of attacks are via phishing emails only. Attackers will either send emails with Malicious File/Malicious Link/spear messages to further get the credentials of the user.
Detections/Prevention of Spear-Phishing emails:
- Build a strong wall as a gateway and reject all the high-score spam emails. Create a custom query to hold all emails which contain malicious files or links.
- Put all the sender addresses is held for previously sent phishing emails from known senders.
Stage 3: Malware developers:
To keep their foothold on the system, the APT group will create malware with the help of malware developers and will insert that malicious code into the system to stay in a long time and to steal the data.
The most APT groups will use the below techniques to stay in the system for time:
- Webshell
- Server Implant
- Computer Spyware
- Mobile Spyware
1-Webshell:
Web shells are malicious scripts that enable threat actors to compromise web servers and launch additional attacks. After penetrating a system or network, threat actors deploy a web shell. They use it as a permanent backdoor into the targeted web applications and any connected systems from this point onwards.
2- Server Implant:
Server implant is nothing but implanting/inserting malicious codes in servers like SSH servers, application servers, Internet-facing servers, etc. If a server is infected, there is a high chance of infecting more machines that all are connecting to the server.
3- Computer/Malware Spyware:
Spyware is a type of malware that installs itself on your device without your knowledge or permission and collects information about you invisibly. It’s monitoring of your personal information might range from displaying annoying advertisements and pop-ups on your device to recording your keystrokes and login credentials.
Scanning the computer with anti-malware software is the best technique to check for spyware. The anti-malware program does a deep scan of the hard drive to identify and eliminate any threats that may be there.
Stage 4: Sysadmins:
Sysadmins are responsible for managing, troubleshooting, licensing, and updating hardware and software assets. They will try to enter the hosts and update website certificates and modify website content and launch unwanted software and will try to update malicious versions.
Stage 5: Exploit Writers:
The exploit is a piece of Software Code written to take advantage of bugs in an application or software. Exploits consist of a payload and a piece of code to inject the payload into a Vulnerable Application. Exploit writers will do one of the following:
- Whether they will exploit an already existing vulnerability to get into the system
- Or, they will exploit the Zero-Day vulnerability
Even though APT group performs many malicious activities, on some occasions, they will have contact with private contractors & Intelligence officers to provide more valuable information in criminal cases.
Also Read: Soc Interview Questions and Answers – CYBER SECURITY ANALYST
Conclusion:
Here we have gone through how the APT group will perform the attack phase by phase. So this is not only the phase of APT, each APT group will have its own techniques and tactics. So just we have gathered some parts here and explained them.



































