Most of the company’s security experts spent days trying to figure out how a hacker could have gotten past the firewall. Now a day’s cyberpunks are more genius in cracking the organization through expert-level skills. As security analysts, it is our responsibility to secure the organization by defending the attacks with strong infrastructure. As per the last year’s attack report, DNS attacks are seen in most of the organizations in all twelve months. Even though DNS attacks are present on the top of the attacks survey, it is proving one good defense service called “DNS Sinkhole”.
What is DNS?
“DNS is kind of the hamster under the hood that drives the internet”
DNS stands for “Domain Name System”. As a human, we can’t memorize all the phone number of our friends, relatives, etc… In the olden days, we used to maintain a phone book to save the numbers. Now technologies have been changed. So what we used to do is, we will save all the phone numbers in our phone directory.
Likewise, we can’t remember every IP of the hostname to reach the website. To save those IP addresses, the DNS concept was introduced in 1985.
How DNS will work?
DNS server will manage massive databases that map a hostname to the IP address and all those will be saved in table format. Whenever we request a hostname from the browser, the DNS will provide us with an exact machine-readable IP address.
For example, if we request xyz[.]com from one of our browsers, First it will check for the IP on the browser cache. If the IP is not available in the cache, next the connection will move to the DNS server. DNS server will search the hostname in the saved table and provide the IP address to the browser. Then the browser will reach the destination xyz[.]com.
What is DNS Sinkhole?
In general firewalls and proxies are used to block malicious traffic across the organization. If it fails, the DNS sinkhole will act as a second level of protection. A sinkhole is a way of redirecting malicious Internet traffic to a fake IP address so that it can be captured and analyzed by security analysts. DNS Sinkhole is used in various organizations to spoof DNS servers to prevent c2c communications towards malicious domains/URLs. This can be attained by configuring the DNS forwarder to return a false IP address to a specific domain/URL.
How does DNS Sinkhole work?
The diagram illustrates the sinkhole operation that occurs when an attacker compromises a user and this infected user tries to contact a botnet.
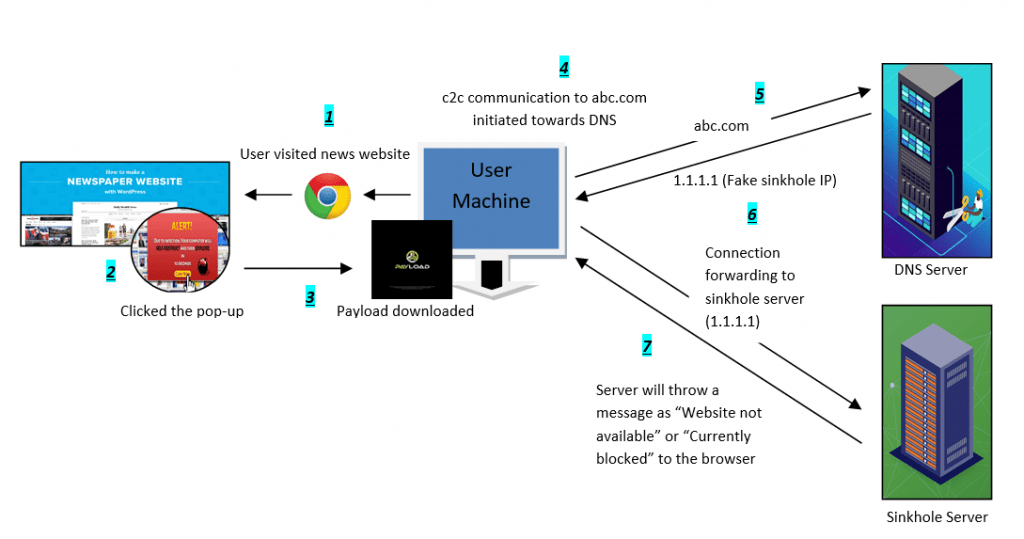
Explanation of DNS Sinkhole Flow:
- In an organization, a user is viewing a news website that has more advertisements, pop-ups, CDN content, etc.
- Suddenly a pop-up appeared for buying a sofa for a low cost. The user has eagerly clicked the pop-up.
- Here, the pop-up was created by an attacker to inject malware via a payload to initiate c2c communication towards the infected server i.e botnet.
- The payload was installed on the machine and the c2c communication via a domain “abc.com” got initiated from the browser.
- The query “abc.com” will make a move towards the organization’s DNS server.
- In the DNS server the actual IP of the domain “abc.com” will be replaced with a fake IP I.e, a sinkhole IP. The sinkhole IP is assigned to a DNS server called sinkhole server where all the c2c domains, DGA domains, recent IOCs will be updated on daily basis. Since the communication is redirected to fake IP which is assigned to a sinkhole server.
- At this stage, the DNS Sinkhole server will act as a defender to stop the c2c communication.
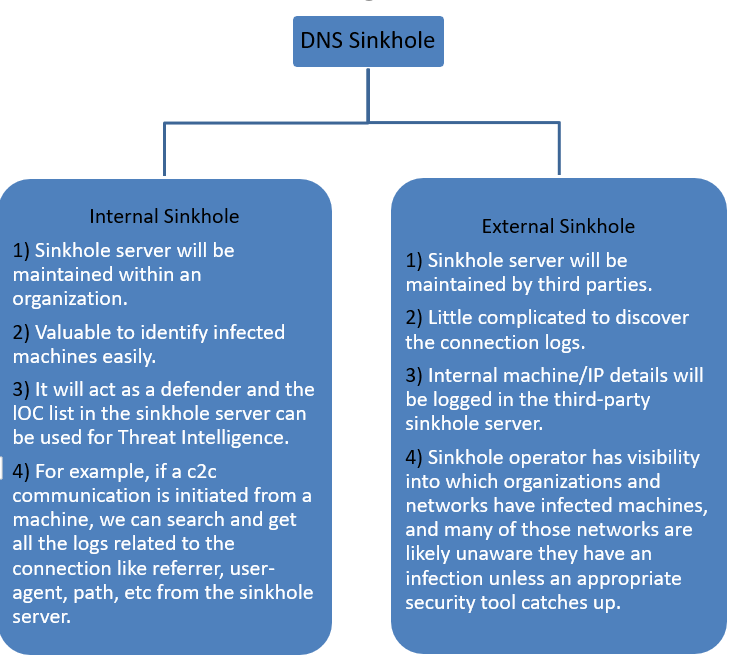
Sinkhole category:
Drawbacks:
Even though sinkhole is a good defense system and simple to execute, more risks and issues are filled along with it.
- A sinkhole can prevent the malicious connection towards the blackhole but a sinkhole won’t prevent it from being executing and spreading to other machines. It can’t mitigate the attack and with help of the sinkhole, malware cannot be removed from the infected machine.
- Before inserting the IOC list into the sinkhole server, the IOCs must be analyzed in advance. Because the IOCs will be collected from open source and may contain false positives.
- Sometimes non-malicious IOCs might be marked as malicious depending on their behavior. This might cause a big issue in an organization by blocking the legit connections.
- If the sinkhole server is maintained within an organization, the server should be isolated or in DMZ. So that the attacker may not aware of the mitigation. Otherwise, the attacker might try to do reverse DNS to change the IPs in the server.
- While maintaining an external sinkhole service, organization details like IP, user agent details, etc will be logged in the third-party server which is like providing all the details of the organization to a mistrustful server. This is considered a criminal act in most jurisdictions.
- If a c2c communication is initiated towards the external sinkhole server, most organization networks are unaware of it. So some sinkhole providers will try to inform the infected machine user by digging on the connection-initiated IP. The users will get panic by seeing those strange activities.
The Effort of a Security Analyst:
As security analysts, we should aware of the drawbacks and need to act according to them. Few points for the security analysts are:
- Have a good knowledge of the organization’s infrastructure & network components.
- Integrate more security tools to quickly capture the unwanted malicious communication to mistrust websites based on the reputation.
- Create a rule in SEIM to get notified if more queries are initiated within a minute or towards the DGA domain. And collect IOCs on a daily basis and upload them to a lookup list and design a rule to capture if any communications initiate towards the IOCs saved in the lookup list.
- Enable rules in security devices like AWS: GuardDuty for sinkhole IP.
- Try to figure out the exact source of the communication to prevent it from spreading to other machines and to check whether it is already open out or not.
Conclusion:
The Sinkhole technique has been around for a while and has been used to prevent malicious connections to the botnet. The technique has both benefits and drawbacks. It’s all in the hands of a security analyst to draw it positively. So we need to understand the ricks behind it and transform it as beneficial in a better way.



































