Defenders who understand privileges and how attackers could abuse them might increase their detection and attack surface reduction capabilities. The most critical aspect of Windows security privileges. We’ll look at how defender needs to safeguard privileges and enhance security in this section.
What is Windows privilege:
A privilege is the right of an account, such as a user or group account, to perform various system-related operations on the local computer, such as shutting down the system, loading device drivers, or changing the system time. Privileges differ from access rights in two ways:
- Privileges control access to system resources and system-related tasks, whereas access rights control access to securable objects.
- A system administrator assigns privileges to user and group accounts, whereas the system grants or denies access to a securable object based on the access rights granted in the ACEs in the object’s DACL.
The privileges held by user and group accounts are stored in an account database in each system. When a user logs in, the system generates an access token with a list of the user’s privileges, including those granted to the user or groups to which the user belongs. It’s important to note that the privileges only apply to the local computer; a domain account can have different privileges on different machines.
When a user attempts to perform a privileged operation, the system examines the user’s access token to see if the user has the required privileges and, if so, whether they are enabled. The system does not perform the operation if the user fails these tests. Most privileges are disabled by default.
Token privileges provide the ability to take certain system-level actions that you only need to do at particular moments. For example, anybody can restart a computer, but the operating system doesn’t enable that privilege by default. Instead, the privilege is enabled when you click Shutdown. You can check the current state of the user’s token privileges using the whoami /priv command. Run as administrator to view full token privileges.
Windows Privilege Abuse: Detection, and Defense:
Totally we have 36 privileges. They are,
| Constant/value | Description |
|---|---|
| SE_ASSIGNPRIMARYTOKEN_NAME TEXT(“SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege”) | Required to assign the primary token of a process. User Right: Replace a process-level token. |
| SE_AUDIT_NAME TEXT(“SeAuditPrivilege”) | Required to generate audit-log entries. Give this privilege to secure servers. User Right: Generate security audits. |
| SE_BACKUP_NAME TEXT(“SeBackupPrivilege”) | Required to perform backup operations. This privilege causes the system to grant all read access control to any file, regardless of the Access Control List (ACL) specified for the file. Any access request other than read is still evaluated with the ACL. This privilege is required by the RegSaveKey and RegSaveKeyExfunctions. The following access rights are granted if this privilege is held: 1) READ_CONTROL 2) ACCESS_SYSTEM_SECURITY 3) FILE_GENERIC_READ 4) FILE_TRAVERSE User Right: Back up files and directories. If the file is located on a removable drive and the “Audit Removable Storage” is enabled, the SE_SECURITY_NAME is required to have ACCESS_SYSTEM_SECURITY. |
| SE_CHANGE_NOTIFY_NAME TEXT(“SeChangeNotifyPrivilege”) | Required to receive notifications of changes to files or directories. This privilege also causes the system to skip all traversal access checks. It is enabled by default for all users. User Right: Bypass traverse checking. |
| SE_CREATE_GLOBAL_NAME TEXT(“SeCreateGlobalPrivilege”) | Required to create named file mapping objects in the global namespace during Terminal Services sessions. This privilege is enabled by default for administrators, services, and the local system account. User Right: Create global objects. |
| SE_CREATE_PAGEFILE_NAME TEXT(“SeCreatePagefilePrivilege”) | Required to create a paging file. User Right: Create a pagefile. |
| SE_CREATE_PERMANENT_NAME TEXT(“SeCreatePermanentPrivilege”) | Required to create a permanent object. User Right: Create permanent shared objects. |
| SE_CREATE_SYMBOLIC_LINK_NAME TEXT(“SeCreateSymbolicLinkPrivilege”) | Required to create a symbolic link. User Right: Create symbolic links. |
| SE_CREATE_TOKEN_NAME TEXT(“SeCreateTokenPrivilege”) | Required to create a primary token. User Right: Create a token object. You cannot add this privilege to a user account with the “Create a token object” policy. Additionally, you cannot add this privilege to an owned process using Windows APIs. Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP with SP1 and earlier: Windows APIs can add this privilege to an owned process. |
| SE_DEBUG_NAME TEXT(“SeDebugPrivilege”) | Required to debug and adjust the memory of a process owned by another account. User Right: Debug programs. |
| SE_DELEGATE_SESSION_USER_IMPERSONATE_NAME TEXT(“SeDelegateSessionUserImpersonatePrivilege”) | Required to obtain an impersonation token for another user in the same session. User Right: Impersonate other users. |
| SE_ENABLE_DELEGATION_NAME TEXT(“SeEnableDelegationPrivilege”) | Required to mark user and computer accounts as trusted for delegation. User Right: Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation. |
| SE_IMPERSONATE_NAME TEXT(“SeImpersonatePrivilege”) | Required to impersonate. User Right: Impersonate a client after authentication. |
| SE_INC_BASE_PRIORITY_NAME TEXT(“SeIncreaseBasePriorityPrivilege”) | Required to increase the base priority of a process. User Right: Increase scheduling priority. |
| SE_INCREASE_QUOTA_NAME TEXT(“SeIncreaseQuotaPrivilege”) | Required to increase the quota assigned to a process. User Right: Adjust memory quotas for a process. |
| SE_INC_WORKING_SET_NAME TEXT(“SeIncreaseWorkingSetPrivilege”) | Required to allocate more memory for applications that run in the context of users. User Right: Increase a process working set. |
| SE_LOAD_DRIVER_NAME TEXT(“SeLoadDriverPrivilege”) | Required to load or unload a device driver. User Right: Load and unload device drivers. |
| SE_LOCK_MEMORY_NAME TEXT(“SeLockMemoryPrivilege”) | Required to lock physical pages in memory. User Right: Lock pages in memory. |
| SE_MACHINE_ACCOUNT_NAME TEXT(“SeMachineAccountPrivilege”) | Required to create a computer account. User Right: Add workstations to domain. |
| SE_MANAGE_VOLUME_NAME TEXT(“SeManageVolumePrivilege”) | Required to enable volume management privileges. User Right: Manage the files on a volume. |
| SE_PROF_SINGLE_PROCESS_NAME TEXT(“SeProfileSingleProcessPrivilege”) | Required to gather profiling information for a single process. User Right: Profile single process. |
| SE_RELABEL_NAME TEXT(“SeRelabelPrivilege”) | Required to modify the mandatory integrity level of an object. User Right: Modify an object label. |
| SE_REMOTE_SHUTDOWN_NAME TEXT(“SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege”) | Required to shut down a system using a network request. User Right: Force shutdown from a remote system. |
| SE_RESTORE_NAME TEXT(“SeRestorePrivilege”) | Required to perform restore operations. This privilege causes the system to grant all write access control to any file, regardless of the ACL specified for the file. Any access request other than write is still evaluated with the ACL. Additionally, this privilege enables you to set any valid user or group SID as the owner of a file. This privilege is required by the RegLoadKey function. The following access rights are granted if this privilege is held: 1) WRITE_DAC 2) WRITE_OWNER 3) ACCESS_SYSTEM_SECURITY 4) FILE_GENERIC_WRITE 5) FILE_ADD_FILE 6) FILE_ADD_SUBDIRECTORY 7) DELETE User Right: Restore files and directories. If the file is located on a removable drive and the “Audit Removable Storage” is enabled, the SE_SECURITY_NAME is required to have ACCESS_SYSTEM_SECURITY. |
| SE_SECURITY_NAME TEXT(“SeSecurityPrivilege”) | Required to perform a number of security-related functions, such as controlling and viewing audit messages. This privilege identifies its holder as a security operator. User Right: Manage auditing and security log. |
| SE_SHUTDOWN_NAME TEXT(“SeShutdownPrivilege”) | Required to shut down a local system. User Right: Shut down the system. |
| SE_SYNC_AGENT_NAME TEXT(“SeSyncAgentPrivilege”) | Required for a domain controller to use the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol directory synchronization services. This privilege enables the holder to read all objects and properties in the directory, regardless of the protection on the objects and properties. By default, it is assigned to the Administrator and LocalSystem accounts on domain controllers. User Right: Synchronize directory service data. |
| SE_SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_NAME TEXT(“SeSystemEnvironmentPrivilege”) | Required to modify the nonvolatile RAM of systems that use this type of memory to store configuration information. User Right: Modify firmware environment values. |
| SE_SYSTEM_PROFILE_NAME TEXT(“SeSystemProfilePrivilege”) | Required to gather profiling information for the entire system. User Right: Profile system performance. |
| SE_SYSTEMTIME_NAME TEXT(“SeSystemtimePrivilege”) | Required to modify the system time. User Right: Change the system time. |
| SE_TAKE_OWNERSHIP_NAME TEXT(“SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege”) | Required to take ownership of an object without being granted discretionary access. This privilege allows the owner value to be set only to those values that the holder may legitimately assign as the owner of an object. User Right: Take ownership of files or other objects. |
| SE_TCB_NAME TEXT(“SeTcbPrivilege”) | This privilege identifies its holder as part of the trusted computer base. Some trusted protected subsystems are granted this privilege. User Right: Act as part of the operating system. |
| SE_TIME_ZONE_NAME TEXT(“SeTimeZonePrivilege”) | Required to adjust the time zone associated with the computer’s internal clock. User Right: Change the time zone. |
| SE_TRUSTED_CREDMAN_ACCESS_NAME TEXT(“SeTrustedCredManAccessPrivilege”) | Required to access Credential Manager as a trusted caller. User Right: Access Credential Manager as a trusted caller. |
| SE_UNDOCK_NAME TEXT(“SeUndockPrivilege”) | Required to undock a laptop. User Right: Remove computer from docking station. |
| SE_UNSOLICITED_INPUT_NAME TEXT(“SeUnsolicitedInputPrivilege”) | Required to read unsolicited input from a terminal device. User Right: Not applicable. |
Some of the Sensitive Privileges are:
- Act as part of the operating system.
- Back up files and directories.
- Create a token object.
- Debug programs.
- Enable computer and user accounts to be trusted for delegation.
- Generate security audits.
- Impersonate a client after authentication.
- Load and unload device drivers.
- Manage auditing and security log.
- Modify firmware environment values.
- Replace a process-level token.
- Restore files and directories.
- Take ownership of files or other objects.
The Privilege Use category logs four events:
4703: A user right was adjusted:
This event generates when token privileges were enabled or disabled for a specific account’s token. As of Windows 10, event 4703 is also logged by applications or services that dynamically adjust token privileges.
4672: Special privileges assigned to new logon:
This event generates new account logons if any of the above sensitive privileges are assigned to the new logon session.
4673: A privileged service was called:
This event generates when an attempt was made to perform privileged system service operations. This event generates, for example, when SeSystemtimePrivilege, SeCreateGlobalPrivilege, or SeTcbPrivilege privilege was used. Failure event generates when service call attempt fails.
4674: An operation was attempted on a privileged object:
This event generates when an attempt is made to perform privileged operations on a protected subsystem object after the object is already opened. This event generates, for example, when SeShutdownPrivilege, SeRemoteShutdownPrivilege, or SeSecurityPrivilege is used. Failure event generates when operation attempt fails.
Also Read : How to Detect Privilege Escalation Attacks and UAC Bypass on Windows
What is Windows EOP?
Windows Elevation of Privilege is a process by which a user obtains a higher level of privilege than that for which he has been authorized. A malicious user may use the elevation of privilege as a means to compromise or destroy a system, or to access unauthorized information.
Here we are going to walk through the Privileges that are frequently abused and hunting tips for detecting it:
SeImpersonatePrivilege:
- Get a handle to a privileged impersonation.
- CreateProcessWithToken
SeTcpPrivilege:
- Call LsaLogonUser ($4U logon) with SeTcpPrivilege and add arbitrary groups to the resulting token.
- Set integrity level to medium.
- Call SetThreadToken to replace our current thread’s token with the new one.
SeAssignPrimaryTokenPrivilege:
- get a handle to privileged impersonation token .
- derive/duplicate a primary token from it .
- CreateProcessAsUser using the new token as an argument to create a new, highly privileged process.
Related concept, kernel structs & APIs:
1-APIs (Few):
- NtQuerySystem Information
- NtSetInformationProcess
- NtSetSecurityObject
- SetNamedSecurityInfo
- LsaLogonUser
- DuplicateTokenEx
- CreateProcessAsUser
- ZwCreateToken
- NtLoadDriver
- SetEntriesInAclA/W
- SetNamedSecurityInfo
- OpenProcessToken
- SetWindowLongPtr
- DeviceloControl
2-Impersonation:
- A user is allowed to impersonate a token even without SeImpersonate Privilege so long as the token is for the same user and the integrity level is less than or equal to the current process integrity level.
3-Kernel mode structs:
- _TOKEN _SEP_TOKEN PRIVILEGES (Present, Enabled, EnabledByDefault privs) EPROCESS.PrimaryTokenFrozen (prevent replacement of existing Primary Token)
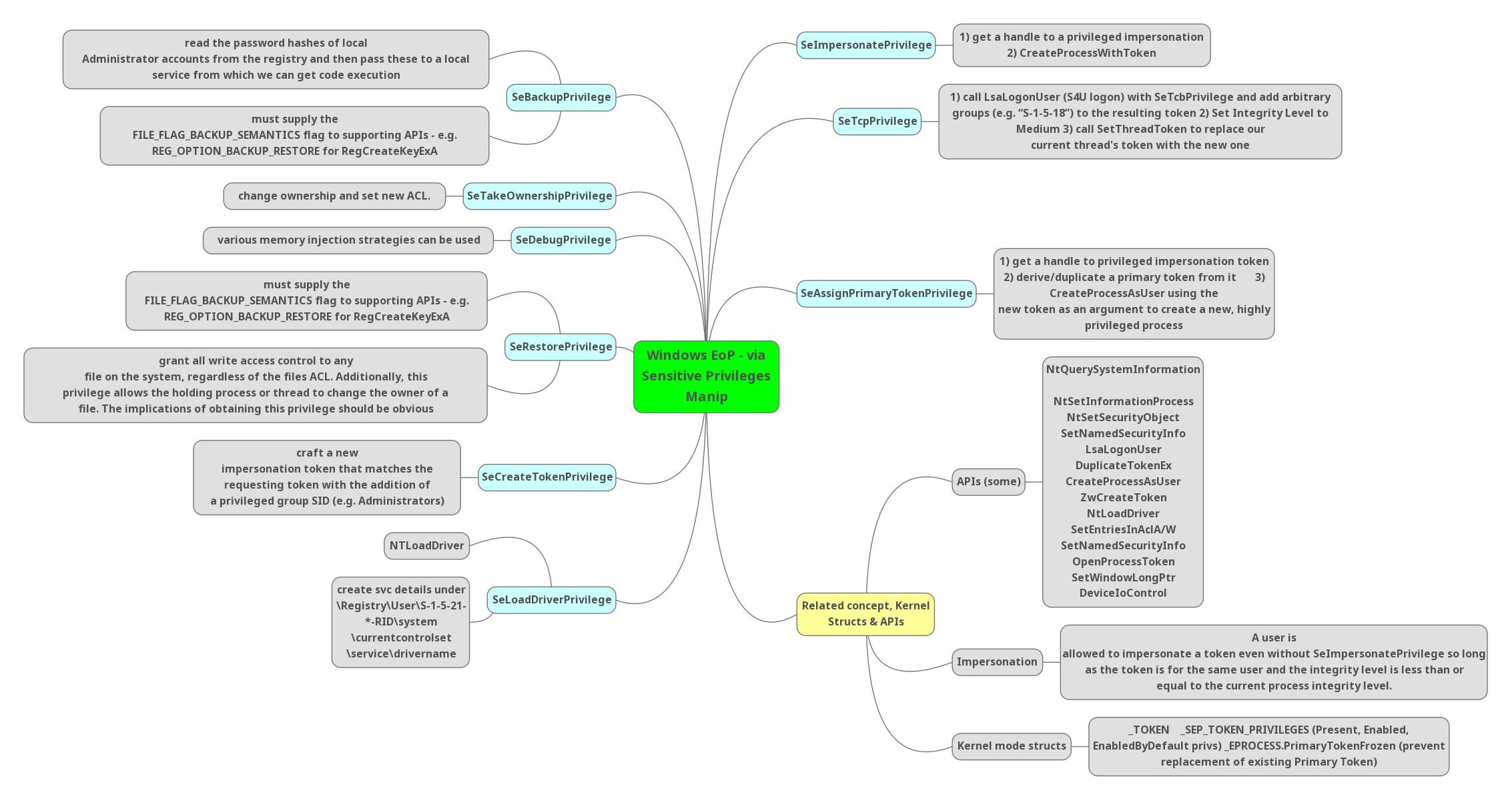
SeBackupPrivilege:
- Read the password hashes of local Administrator accounts from the registry and then pass these to a local service from which we can get code execution
- Must supply the FILE_FLAG_BACKUP_SEMANTICS flag to supporting APIs – e.g. REG OPTION_BACKUP_RESTORE for RegCreateKeyExA
SeTakeOwnershipPrivilege:
- Change ownership and set new ACL.
SeDebugPrivilege:
- Various memory injection strategies can be used.
SeRestorePrivilege:
- Must supply the FILE_FLAG_BACKUP_SEMANTICS flag to supporting APIs – e.g. REG OPTION BACKUP RESTORE for RegCreateKeyExA
- Grant all write access control to any file on the system, regardless of the files ACL. Additionally, this privilege allows the holding process or thread to change the owner of a file. The implications of obtaining this privilege should be obvious
Also Read: Threat Hunting using Firewall Logs – Soc Incident Response Procedure
SeCreateToke Privilege:
- Craft a new impersonation token that matches the requesting token with the addition of a privileged group SID (e.g. Administrators)
SeLoadDriverPrivilege:
- NTLoadDriver
- Create svc details under
- \Registry\User\S-1-5-21-*-RID\system
- \currentcontrolset
- \service\drivername
Conclusion:
Learning windows privilege will take more time, but once it is established as rules, defending will be at its best. Privilege is the first defacement of an attack that is performed. So, after going over the criteria mentioned, enable rules based upon your organization.



































