What is Threat Intelligence?
In the world of cybersecurity, APT(Advanced persistent threats) and Defenders(Blue teamers) are constantly trying to outmaneuver each other. To get the data on the threat and threat actor’s next move, a defender should know the big picture of that threat, such as: when? why? and how? For this, an organization gets benefits from threat intelligence.
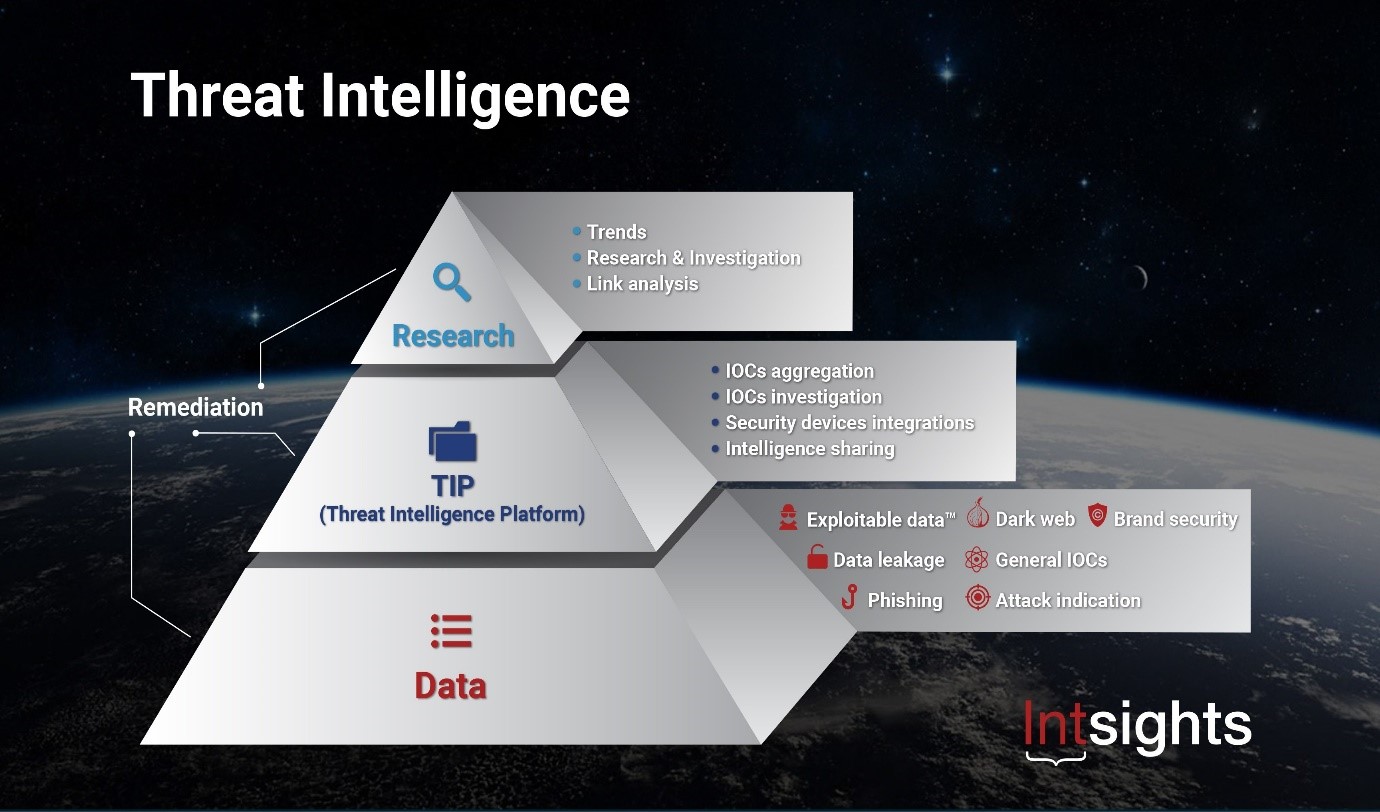
Threat intelligence is information that is collected from various sources to determine the motivations, targets, and TTP ( tactics, techniques, and procedures) of cyber attacks and cyber threat actors that may be against your organization. Technically, threat intelligence is the database of threat actors’ behaviors such as attacker IPs, Domains, Hashes, and tools & techniques which is known to ae IOC(indicators of compromise).
Threat intelligence sources:
You need multiple sources of intelligence to get a complete picture of the actual threat.
- Threat feeds
- Media
- Darkweb
- Open web
- Network event logs.

CTI Life cycle:
- Planning– Determine the purpose,objective and requirements of CTI.
- Collection– Collecting data from various sources
- Processing- Process the collected information and make it ready for anlaysis.
- Analysis– Analysing the data and transforming it into intelligence and making it ready for sharing.
- Dissemination– Sharing threat intellegince data
- Feedback– Acquire and analyse stakeholder feedbacks.
Types of CTI
1.Tactical CTI:
It is usually employed for protecting the network. Their job is mostly technical and provides details on the latest threats— what tactics or techniques, procedures are practiced by the specific attacker. They look for IOCs and IP addresses for evidence, URLs, system logs to detect upcoming data breach attempts.
People or products who use this CTI are
- SOC Analyst
- Security products(IDS/IPS/Firewall)
- SIEM products
Also Read: Threat Hunting using Proxy Logs – Soc Incident Response Procedure
2.Operational CTI:
They are the adviser of IT defenders understanding the nature of cyberattacks, simultaneously explaining attackers’ intent, timing, and uniqueness of the attacking individual or group.
People or products who use this CTI are
- Threat Hunters
- Incident responders
- Security Engineers
3.Strategic CTI:
They provide a detailed analysis of trends and emerging risks to create an overall picture of the possible consequences of a cyber attack.
People or products who use this CTI are
- C level executives
- Managers
Evolution of Threat Intelligence:
For this, we should know the answer to the below question!!
How do cybersecurity companies work on Threats?
Let’s take the example of company A using an antivirus solution. One not so fine day, one of the machines starts behaving weirdly like consuming high resources. When the administrator inspects the issue, he came to know one process is eating up all the CPU and memory. After further examination, he found it malicious then he raised his concerns to the antivirus company.
Antivirus companies will split it into three-phase to identify and update the threats.
1.Malware analysis-After hash is derived from the malicious file and through the various dynamic and static analysis technique, the behavior of the malware is identified.
For eg: Consider the particular malware as spyware designed to download payload from 163.45.10.1(IP address), and it looks for sensitive data, copy the data from the system and send it to [email protected] (Email id).
After analyzing, now the vendor can get the filename, hash value, IP address, and mail Addresses of the threat actors. These artifacts are called IOC’s and they will update into the database.
2.Developing the signature –Develop a unique signature for that particular threat.
3.Testing –to ensure that signature does not detect any legitimate files.
Tested signatures will be updated to the server and they will be distributed to all the other customers. Now, the updated IOCs are Threat intelligence.
PYRAMID OF PAIN(for the attacker)
If you are going to use the only hash value, IP address for threat detection, attackers going to step ahead of you, they can easily change the hash value and IP address and use different tools and techniques to attain their motive. So try to find as many as details like attacker tools, techniques. These are all difficult for an attacker to change from one attack to another.
Also Read: What is the MITRE ATT&CK Framework? How Is It Useful
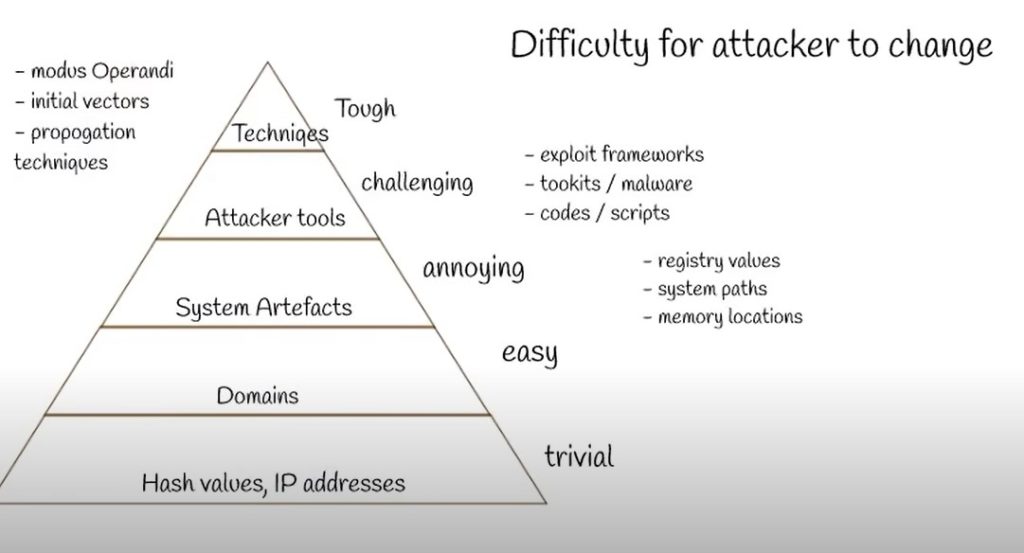
By fetching all the details on the pyramid, we are on the track and expertise in threat intelligence and it will be useful to get the full picture of the threat and threat actors.
How to get to the top of the pyramid?
- Set up own honeypot network.It will enable you to monitor the activities of an attacker.By this,you came to know the tools and techniques which are used by an attacker.
- Set up malware lab and analyse malware to understand the system artifacts.
- Analyse darkweb for any intellectual data breaches.Use dark web monitoring service.
CONCLUSION:
The following diagram illustrates how, without open data sharing, multiple organizations may be targeted by the same attacker, and each must detect and respond to the attack independently. By using an open-source threat database, once one organization is attacked, everyone is aware of the risk and able to easily identify and defend against the attacker.
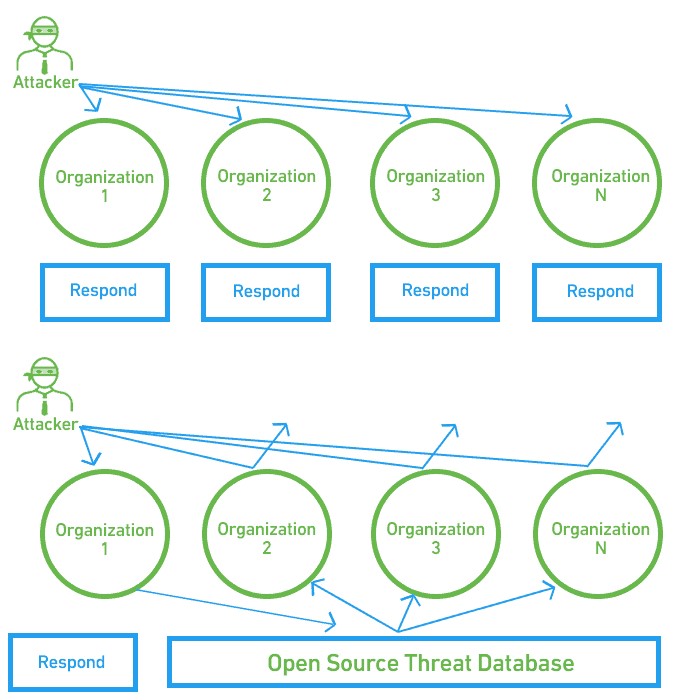
CYBER ATTACK RESPONSE WITH AND WITHOUT THREAT INTELLIGENCE



































